فهرست مطالب
Biolmpacts
Volume:9 Issue: 2, Jun 2019
- تاریخ انتشار: 1398/02/01
- تعداد عناوین: 7
-
-
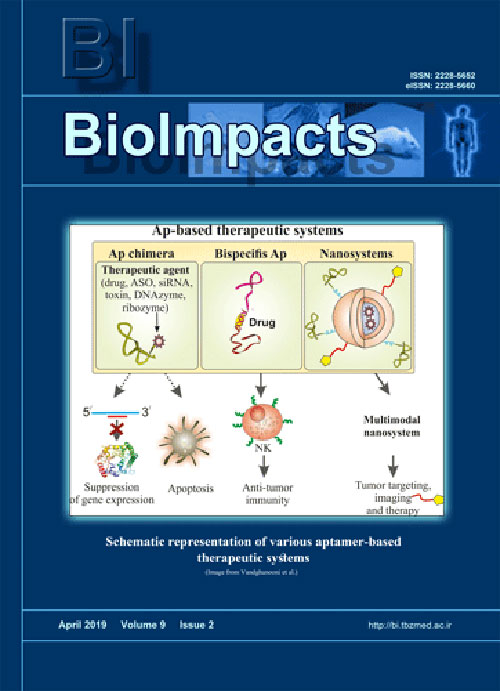
Pages 67-70Aptamers (Aps) are short single-strand nucleic acids exhibiting unique 3D structure which facilitate their targeting potential against various cancer molecular markers (CMMs). Such features of Aps not only make them as suitable targeting agents in targeted drug delivery systems (DDSs) but also candidate them as macromolecules that inhibit the interaction of the target protein with other proteins. On the other hand, the conjugation of Aps with another therapeutic molecule such as antisense oligonucleotide (AS-ODN), siRNA/miRNA, Ap, toxins, chemotherapeutic agents, DNAzyme/Ribozymes provide hopeful strategy to eradicate the malignancies and overcome the off-target unwanted side effects. Such prominent features of Aps make them a promising treatment modality to overcome the tumor complexity and heterogeneity and consequently hired toward personalized therapy of cancer by using bispecific Ap-based therapeutics.Keywords: Aptamer, Aptamedicine, Nanomedicine, Drug delivery systems, Personalized medicine, Cancer therapy
-
Pages 71-78IntroductionThe detection of micrometer-sized particles like cells is limited by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors because of having the depth of evanescent wave <500 nm. In this study, for the first time, we exhibited the use of streptavidin functionalized gold nanorods as intensification labels for detection of cell surface markers in SPR based biosensors.MethodsThe gold nanorods (ʎ max: 735nm ) was modified with streptavidin using EDC/NHS coupling method and Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) was selected as cell model for detecting VE- cadherin on cell surface using real time SPR device in the 785 nm wavelength of laser source.ResultsThe investigations revealed that the plasmonic field extension produced from the gold layer and gold nanorods results in multiple enhancement of SPR signals when the wavelength of laser source in SPR instrument is matched with the wavelength of maximum absorbance in gold nanorods. Also the results show that the growth of ∆RU value in specific and non-specific binding for various cell number injection are produced with increasing the cell number.ConclusionThe results displayed that cell detection can be performed in real- time form without any need of a time- consuming process used in conventional methods like immunocytochemistry, flow cytometry and western blotting.Keywords: enhanced-surface plasmon resonance, cell detection, VE-cadherin, gold nanorods
-
Pages 79-88IntroductionDocumentation on the potency of chromones as acetylcholinesterase (AChE) antagonists has paved the way for designing and usage of novel chromone derivatives as AChE inhibitors modelled on the cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Here, two minimally substituted chromones, namely 3-cyanochromone (CyC) and 7-amino-3-methylchromone (AMC) were checked for their AChE inhibition efficacies and plasma protein modulation.MethodsColorimetric enzymatic assay as well as fluorescence measurements was performed for obtaining the experimental results, which were further corroborated by molecular docking and simulation studies.ResultsThe investigated systems exhibited strong inhibition activities against AChE, with CyC (IC50= 85.12 ± 6.70 nM) acting as better inhibitor than AMC (IC50 = 103.09 ± 11.90 nM) and both having IC50 values in the range of FDA approved cholinergic drug Donepezil (IC50 = 74.13 ± 8.30 nM). Non-competitive inhibition was observed in both the cases with the inhibitors binding near the peripheral anionic site (PAS) of AChE. Having a planar nitrile group in CyC as compared to sp3 hybridised substituents in AMC facilitated stacking interactions in the former, accounting for its higher inhibitory efficacy. A significant decrease in the inhibition potency of CyC (~32%) was noted in comparison with AMC (~5%) when the experimental medium was switched from buffer to human serum albumin (HSA) matrix.ConclusionThis comparative study affirms the importance of meticulous substitution in the chromone scaffold to promote maximum inhibition potency, while considering their usage as AD drugs.Keywords: acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition, chromones, thioflavinT fluorescence, PAS binding, AD drug, Stacking interactions
-
Pages 89-95IntroductionFocal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), the most common primary glomerular disease, is a diverse clinical entity that occurs after podocyte injury. Although numerus studies suggested molecular pathways responsible for development of FSGS, many unknowns still remain about its pathogenic mechanism. Two important pathways were predicted as candidates for pathogenesis of FSGS in our previous in silico analysis that we aim to confirm these pathways experimentally in the present study.MethodsThe expression level of four enzyme genes that are representative of "chondroitin sulfate degradation" and "eicosanoid metabolism" pathways were investigated in the urinary sediment of biopsy proven FSGS patients and healthy subjects using real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). These target genes were arylsulfatase, hexosaminidase, cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin I2 synthase. The patients were sub-divided into two groups based on range of proteinuria and glomerular filtration rate and were compared for variation in the expression of target genes. Correlation of target genes with clinical and pathological characteristics of the disease was calculated and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed.ResultsA combined panel of arylsulfatase, hexosaminidase and cyclooxygenase-2 improved the diagnosis of FSGS to 76%. Hexosaminidase was correlated with the level of proteinuria, while cyclooxygenase-2 was correlated with interstitial inflammation and serum creatinine level in the disease group.ConclusionOur data supported the implication of these target genes and pathways in the pathogenesis of FSGS. Besides, these genes can also be considered as non-invasive biomarkers for FSGS.Keywords: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, molecular pathway, biomarker
-
Pages 97-103IntroductionThe effect of a bare-metal stent on the hemodynamics in the main branch of a coronary artery bifurcation with a particular type of stenosis is numerically investigated by the Computational Fluid Dynamics.MethodsThree-dimensional idealized geometry of bifurcation has been constructed in Catia modelling commercial software package. The Newtonian blood flow is assumed to be incompressible and laminar. Computational Fluid Dynamics has been utilized to calculate the shear stress and blood pressure distributions on the wall of main branch. In order to do the numerical simulations, a commercial software package named as COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3, has been employed. Two types of stent, namely, one-part stent and two-part stent have been applied to prevent the build-up and progression of the atherosclerotic plaques in the main branch.ResultsA particular type of stenosis in the main branch have been considered in this research. It occurs before and after the side branch. It was found that the main branch with an inserted one-part stent has the smallest region with the wall shear stress below 0.5 Pa which is the minimum wall shear stress in the main branch without the stenosis.ConclusionIt is recommended to use a one-part stent in the main branch of a coronary artery bifurcation for the aforementioned type of stenosis in it.
Keywords: Coronary Artery Bifurcation, Hemodynamics, Stent, Computational Fluid Dynamics -
Pages 105-113IntroductionValproic acid (VPA) is a well-established anticonvulsant drug that has been increasingly used in the treatment of many forms of generalized epilepsy. Although there are many reports of adverse effects of VPA, studies focusing on the concentration–response relationships of VPA and its metabolites in patients with refractory epilepsy are extremely limited. In this paper, a high efficient method was developed for the extraction, preconcentration, and determination of valproic acid and its main metabolite in plasma.MethodFor the extraction and preconcentration of the selected analytes, a volume of an extraction solvent was placed at the bottom of the microtube containing pretreated plasma. The mixture was rapidly withdrawn into a 1-mL syringe and then pushed-out into the tube in order to form a cloudy mixture. For the further turbidity, the mixture was shaken on a vortex agitator.ResultThis procedure was used to analyze plasma samples of Iran patients with epilepsy (n = 70). The results revealed that in most patient with low level of valproic acid relative to expected level of valproic acid, amount of 3-heptanone was high. The limits of quantification of the valproic acid and 3-heptanone were obtained 0.2 mg L–1 and 0.04 mg L–1, respectively. An acceptable precision was obtained for the concentrations of 2 mg L-1 each analyte (relative standard deviation ≤ 9 %).ConclusionThe obtained results showed that this method is simple, sensitive and reliable and can be used for analysis of the selected analytes in plasma sample of patient with epilepsy.Keywords: Gas chromatography, Valproic acid, 3-Heptanone, Plasma, Microextraction method
-
Pages 115-121IntroductionFlavonoids are widely used as a dietary supplement and thus occupy a significant role in the research field. In recent time interaction of flavonoid-metal complexes with serum, albumins (SAs) are widely studied among researchers since the complexation have a significant impact on the biological activities. Additionally, the binding nature of flavonoids with serum albumins gets modified in the presence of metal ions.MethodsIn the present review we have studied every interaction of Quercetin (Qu), a well-known flavonoid, and its Cu2+ complexes with SA to provide sufficient information about the beneficial role of metal-flavonoid complexes over free flavonoids.ResultsComplexation with Cu(II) ion more or less altered the mode of binding of Qu with SAs. The strength of binding increased in the presence of Cu(II) as evident from the binding constant calculation. But the drug binding site in (bovine serum albumin (BSA) and human serum albumin (HSA) are not altered during the complexation process.ConclusionTo enhance the pharmaceutical outcomes of Qu molecule one may use Qu-Cu(II) complex for development and delivery of the small molecule into the serum albumins.Keywords: Quercetin, Copper, Serum albumin