فهرست مطالب
Biolmpacts
Volume:5 Issue: 3, sep 2015
- تاریخ انتشار: 1394/09/05
- تعداد عناوین: 7
-
-
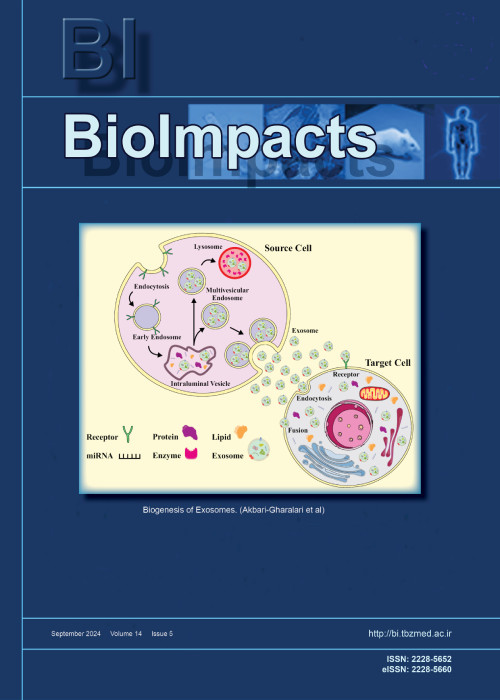
Page 117ntroduction: Exosomes (EXOs) and ectosomes (ECTOs) are nanoscale membranous extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from different cells mediating various cellular communications. EXOs are liberated based on the exocytosis of multivesicular bodies، while ECTOs are ubiquitously released from the plasma membranes.MethodsHere، in this paper، we go over the extracellular vesicular machineries and concisely highlight their clinical importance in solid tumors and their possible applications in cancer immunotherapy/vaccination.ResultsIn various types of cancers، these vesicles play central roles delivering cancer cell messages to the target cells، as a result both of them seem to provide a novel useful means for diagnosis and therapy of malignancies. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes (DEXOs) are able to activate the tumor antigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) and hence induce antitumor responses in vivo. Within the tumor microenvironment (TME)، however، tumor cells seem to generate exosomes (the so-called oncosoems) that may act in favor of tumor progression.ConclusionsAs complex systems، these vesicular micro-/nano-machines convey important cellular messages dependent upon the cells/tissue setting (s). In addition to their potential in diagnosis of cancers، they have been exploited for cancer immunotherapy/vaccination. However، such treatment strategies need to be carefully designed to attain desired clinical outcomes.Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy Cancer vaccination Exosomes Extracellular vesicles Vesicular trafficking
-
Page 123Despite very wide variations of malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations in biological samples, it is still used as a biomarker of oxidative stress in clinical investigations. In the current perspective study, we aimed to summarize a number of critical analytical points for determination of MDA. Technical problems and controversial findings in healthy people and some psychiatric disorders reveal that the reliability of MDA as a biomarker of oxidative stress needs to be re-evaluated by experts.Keywords: Thiobarbitoric acid reac, tive substances Oxidative stress Biomarker
-
Page 129IntroductionThe main objective of this study was to investigate the possibility of replacing electrophoresis cross-linker with non-electrophoresis N, N′-methylenebisacrylamide (BIS) in N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAM) polymer gel and its possible effect on dose response.MethodsNIPAM polymer gel was prepared from non-electrophoresis grade BIS and the relaxation rate (R2) was measured by MR imaging after exposing the gel to gamma radiation from Co-60 source. To compare the response of this gel with the one that contains electrophoresis grade BIS, two sets of NIPAM gel were prepared using electrophoresis and non-electrophoresis BIS and irradiated to different gamma doses.ResultsIt was found that the dose–response of NIPAM gel made from the non-electrophoresis grade BIS is coincident with that of electrophoresis grade BIS.ConclusionTaken all, it can be concluded that the non-electrophoresis grade BIS not only is a suitable alternative for the electrophoresis grade BIS but also reduces the cost of gel due to its lower price.
-
Page 135IntroductionThe risk of drug resistance and the use of medicinal plants in malaria prevention and treatment have led to the search for new antimalarial compounds with natural origin.MethodsIn the current study, six extracts with different polarity from aerial parts and rhizomes of Eremostachys macrophylla Montbr. & Auch., were screened for their antimalarial properties by cell-free β-hematin formation assay.ResultsDichloromethane (DCM) extracts of both parts of plant showed significant antimalarial activities with IC50 values of 0.797 ± 0.016 mg/mL in aerial parts and 0.324 ± 0.039 mg/mL in rhizomes compared to positive control (Chloroquine, IC50 = 0.014 ± 0.003 mg/mL, IC90 = 0.163 ± 0.004 mg/mL). Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the most potent part (DCM extract of rhizomes) by vacuum liquid chromatography (VLC) afforded seven fractions. Sixty percent ethyl acetate/n-hexane fraction showed considerable antimalarial activity with IC50 value of 0.047 ± 0.0003 mg/mL.ConclusionFrom 6 extracts with different polarity of E. macrophylla,s aerial parts and rhizomes, the DCM extract of both parts were the most active extract in this assay. The preliminary phytochemical study on the VLC fractions of the most potent part persuades us to focus on purifying the active components of these extracts and to conduct further investigation towards in vivo evaluation.
-
Synthesis and characterization of dextran coated magnetite nanoparticles for diagnostics and therapyPage 141IntroductionExpansion of efficacious theranostic systems is of pivotal significance for medicine and human healthcare. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are known as drug delivery system and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent. MNPs as drug carriers have attracted significant attention because of the delivery of drugs loaded onto MNPs to solid tumors, maintaining them in the target site by an external electromagnetic field, and subsequently releasing drugs in a controlled manner. On the other hand, it is believed that MNPs possess high potential as MRI contrast agents. The aim of this work was to payload curcumin into dextran coated MNPs and investigate their potential as theranostic systems for controlled drug delivery and MRI imaging.MethodsMNPs were synthesized as a core and coated with dextran as polymeric shell to provide steric stabilization. Curcumin as anticancer drug was selected to be loaded into NPs. To characterize the synthesized NPs, various techniques (e.g., DLS, FESEM, FT-IR, XRD, and VSM) were utilized. In vitro drug release of curcumin was evaluated at 37˚C at the pH value of 5.4 and 7.4.The feasibility of employment of dextran coated MNPs as MRI contrast agents were also studied.ResultsFormulations prepared from dextran coated MNPs showed high loading (13%) and encapsulation efficiency (95%). In vitro release study performed in the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH= 7.4, 5.4) revealed that the dextran coated MNPs possess sustained release behavior at least for 4 days with the high extent of drug release in acidic media. Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) analysis proved the superparamagnetic properties of the dextran coated MNPs with relatively high-magnetization value indicating that they were sufficiently sensitive to external magnetic fields as magnetic drug carriers. Furthermore, dextran coated MNPs exhibited high potential as T2 contrast agents for MRI.ConclusionBased on our findings, we propose the dextran coated MNPs as promising nanosystem for the delivery of various drugs such as curcumin and MRI contrast agent.
-
Page 151IntroductionHuman health is deemed to be maintained by the crosstalk among the body and probiotic bacteria. Disruptions in this composition are associated with the pathogenesis of numerous diseases. Through modernization, traditional foods consumption has been abandoned and native food starters have been substituted with industrial products. Hence, we aimed to isolate and evaluate probiotic bacteria from traditional fermented foods which can be used as probiotics as well as starter cultures in food industry and in medicine against antibiotic resistant pathogenes. To this end, an intact village was recognized in the Republic of Azerbaijan with traditional dairy products, yielding a variety of potential probiotics.MethodsIn this study, tvorog as a traditional dairy product from Dashkasan, Ismailli and khachmaz regions in Azerbaijan was characterized for the isolation of Lactobacilli with probiotic potentiality. The bacteria were tested for the resistance to the acid, bile, and the antagonistic effect of human pathogenic bacteria. The isolates were identified by 16s rDNA sequencing with a blast to the databank.ResultsThree species with higher homology to the L. planetarium, L. rhamnosus, and L. casei with high probiotic potentiality and antibacterial effects were isolated.ConclusionHomemade tvorog curd cheese in Azerbaijan harbor a variety of probiotics with industrial applications as well as potentiality to be preserved in a biobank for the future medicinal applications especially against antibiotic resistant pathogenes.
-
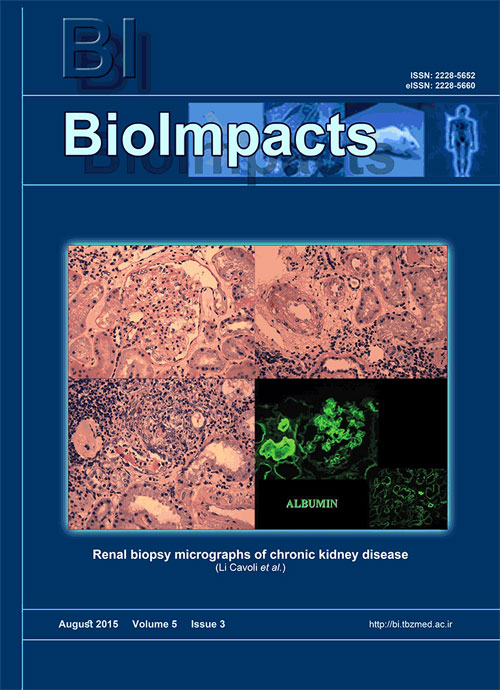
Page 155IntroductionThe metabolic syndrome (MS) encompasses many metabolic abnormalities and the insulin resistance is considered as one of the most significant denominators. The chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an emerging health problem but only few patients would reach the end stage renal disease. There exists an increasing strong association between MS and CKD, but up until now the link between MS and CKD is unclear and there are few studies regarding therenal histology in MS.MethodsWe describe an acute tubulointerstitial nephritis case, due to both infective and pharmacological aetiology, overlapping relevant histological changes (focal segmental glomerulosclerosis [FSG], hyaline arteriosclerosis) in a patient with MS and previously normal renal function. Despite the severe vascular finding (elevated renal arterial resistive index), the patient recovered a normal renal function.ResultsWe reviewed the kidney pathological studies in MS and analyzed the principal renal histological images of glomerulomegaly, segmental glomerulosclerosis, and obesity-related glomerulopathy.ConclusionDespite the strong association, the renal involvement in MS has not been proven. A greater knowledge of the combination of histological renal changes in MS can help to understand the pathophysiological mechanism(s) of MS.