فهرست مطالب
Journal of Translational Research in Urology
Volume:4 Issue: 2, Spring 2022
- تاریخ انتشار: 1401/04/09
- تعداد عناوین: 8
-
-
Pages 54-56
It has been a while since chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy was introduced as an attractive immunotherapeutic approach to fighting cancer. Despite the remarkable success of this approach in treating blood malignancies such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), treatment of solid cancers such as bladder cancer still has many challenges and problems. This work highlights CAR-based cell therapy's preclinical and clinical studies in bladder cancer, their successes, and the challenges involved in translating this procedure into the clinic.
Keywords: CAR-T cell therapy, Bladder Cancer, Immunotherapy, clinical trials -
Pages 57-60Introduction
One of the uncommon diseases and serious one in an infant is hyponatremia with hyperkalemia. Secondary Pseudo hypoaldosteronism (PHA) is congenital adrenal hyperplasia that has been described in babies with urinary tract infection (UTI) and urinary tract malformation (UTM).
Case presentationHere, we report a CRE guideline-based case of a 39 days infant with failure to thrive and lastly identified with transient PHA because of UTI with posterior urethral valves. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia was excluded in front of cortisol; 17 OH progesterone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) were within normal ranges. The infant was put under double antibiotic and sodium replacement therapy and cation exchange resin at the rate of one gram per kilogram, and after stabilizing his clinical condition and sterilizing the urine, the infant underwent endoscopic valve resection.
ConclusionTransient secondary type 1 PHA caused by a UTI should be considered in the existence of hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and metabolic acidosis in newborns with UTI and UTM.
Keywords: Secondary PAH, Infant, Urinary tract infection, Posterior Urethral Valves -
Pages 61-70
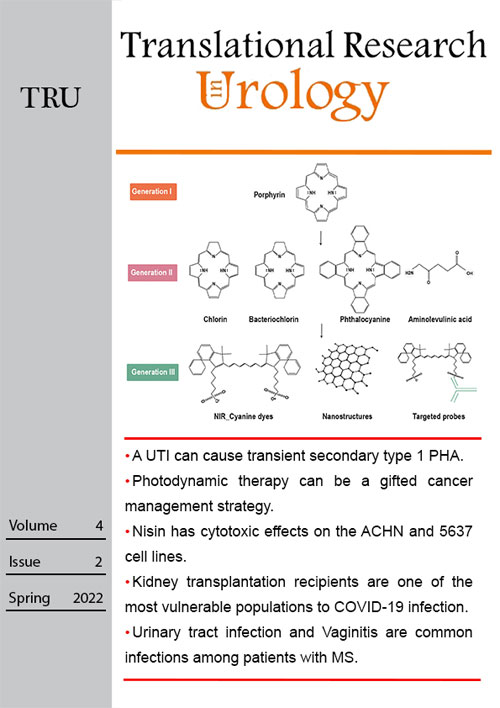
Photodynamic therapy is a novel approach to cancer treatment. It is based on reactive oxygen species production by light illumination on the photosensitizer in the presence of molecular oxygen. The photosensitizer is a non-toxic agent activated by light with a specific wavelength and leads to ROS production and increased oxidative stress in cancer cells to kill them. For treating the patient, after administration of photosensitizer, it distributes to different organs and the tumor environment. The photodynamic actions happen with illuminating light on the tumor's location, and the tumor will be destructed. In this review, we introduce the mechanisms of photodynamic therapy and its components.
Keywords: Photodynamic therapy, Cancer treatment, Photosensitizer -
Pages 71-76IntroductionShock wave lithotripsy (SWL) is a less-invasive procedure for treating a subgroup of renal stones. Since it may cause significant pain and anxiety during the procedure, several strategies have been proposed to reduce the discomfort during the SWL procedure. This study aimed to evaluate transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) as a non-invasive analgesic strategy during SWL.MethodsA total of seventy-nine patients who underwent the SWL were included. The participants were randomly divided into two groups: the case group using conventional TENS (41 patients) and the control group without TENS. The visual analog scale (VAS) was recorded at the end of the SWL session. The analgesic (30mg ketorolac) was given in both groups due to the patient's request.ResultsBoth study groups were similar in age, sex, BMI, history of SWL, hypertension, stone location, and stone size. Our data indicated less VAS in the case group than in the control group throughout the procedure, although it was not statistically significant (P-value=0.087).ConclusionTENS can be offered as a non-invasive and safe pain relief strategy during the SWL.Keywords: extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, urolithiasis, Pain
-
Pages 77-82Introduction
Kidney transplantation recipients are one of the most vulnerable populations to COVID-19 infection and are more prone to develop complications. The lower urinary tract might be seriously affected by COVID-19 disease in this population. The present study aimed to assess the impact of COVID-19 disease on LUTS in kidney transplantation recipients.
MethodsAll patients who underwent kidney transplantation at Sina Hospital (Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran) were included in this cross-sectional study. Covid-19 infection was confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of oropharyngeal swabs. All patients with urinary tract infections were excluded from the study. LUTS status was assessed by International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS).
ResultsThe study involved 153 consecutive kidney transplant recipients; 67 (43.8%) and 86 (56.2%) patients were with and without Covid-19, respectively. The mean age of all patients was 49.7±12.9 years, and 105 (68.6%) males were in the study. The mean IPSS in kidney transplant recipients with and without Covid-19 was 2.74±3.0 and 1.96± 2.7, respectively. A significant difference was observed in IPSS between patients with and without Covid-19 (P-value=0.03). The kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 had a higher risk of moderate IPSS (OR: 1.5 CI 95%: 0.5-4.87) than those without COVID-19, but it is not significant (P-value=0.4).
ConclusionWe pioneering found that LUTS in kidney transplant recipients measured by the validated tool IPSS was significantly more intense in those affected by COVID-19 infection. Future studies are necessary to explore t long-term impact and potential sequels.
Keywords: Lower Urinary Tract Symptom, COVID-19, Kidney Transplantation, SARS-CoV-2 -
Pages 83-88IntroductionCancer is considered a significant cause of mortality worldwide, and the mortality rate has been growing significantly in the last decades. The present study aimed to assess the effect of nisin on apoptosis and metastasis of human bladder carcinoma (5637) and renal carcinoma (ACHN) cells.MethodsIn this experimental study, the 5637 and ACHN cell lines were cultured and treated with diverse densities of nisin. The viability test was evaluated by MTT assay. The gene expression level of BAX, BCL-2, CEA, and Rho-GDI2 was examined by real-time PCR.ResultsThe 430 and 230µg/mL nisin could suppress the proliferation of ACHN and 5637 cell lines, respectively. In both studied cancer cells, the expression of BAX, BCL-2, CEA, and Rho-GDI2 genes was significantly augmented with nisin exposure.ConclusionOur results discovered that nisin has cytotoxic effects on the ACHN and 5637 cells and prompts apoptosis over up-regulating the BAX/BCL-2 ratio in the 5637-cell line. Moreover, nisin might suppress the metastasis process via up-regulation of the Rho-GDI2 gene.Keywords: Antimicrobial Peptides, Anticancer, Apoptosis, Gene expression, Real-Time PCR
-
Pages 89-97IntroductionThis study aimed to investigate the effect of black seed and hydroalcoholic honey extract on changes in serum, urine, and kidney tissue variables in male mice with kidney stones.MethodsTo do this, 7 groups were first considered, which are: harmful and healthy control groups, treatment with concentrations of 125 and 250mg/kg black seed, treatment with concentrations of 125 and 250 mg/kg Honey, and treatment with 125 mg/kg black seed with 125 mg/kg honey. The required substances were introduced to the groups from the first to the last day of the experiment, and 1 % ethylene glycol was added to the drinking water. The researchers looked at serum variables, including potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium, urine factors like citrate, oxalate, and calcium, and tissue factors like kidney weight and crystal count.ResultsThe results of this study showed that the accumulation of calcium oxalate crystals in the negative control group increased significantly (P-value<0.001) compared to the combined group of honey and black seed at 125 mg/kg (without crystal accumulation). In addition, in other groups, the number of rock accumulations significantly decreased compared to the negative control group (P-value<0.001). Biochemical examination of urine at the end of the experiment showed a significant decrease (P-value<0.001) in urinary oxalate in the combined group of honey and black seed 125 mg/kg (0.3±0.07). Urine calcium concentration also decreased significantly (P-value<0.05). In the combined group, honey and black seed had 125 mg/kg (5.70±0.75). In addition, serum and tissue parameters in the honey and black seed groups alone (125 and 250 mg/kg) and the honey and black seed group (125 mg/kg) showed significant changes in the prevention and treatment of kidney stones.ConclusionThe combination of black seed and honey is a viable option for kidney stone prevention and therapy, which shows the synergistic effects of honey and black seed with each other.Keywords: Kidney Stones, Black Seed, honey, Serum, Urinary Factors
-
Pages 98-103Introduction
Urinary tract infection (UTI) and vaginitis are common urological conditions societies have dealt with for decades. UTIs can have certain predisposing factors. Multiple sclerosis (MS) and Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs), primary MS treatment regimens, demonstrate the effects of MS and DMTs on urological complications.
MethodThis paper is a cohort study conducted from June 2020 to October 2021 using prospectively collected data from Every patient registered at Tehran's Multiple Sclerosis Referral Research Center. This study's inclusion criteria consisted of patients diagnosed with MS based on McDonald criteria and exposed to DMTs for at least six months. The exclusion criteria were being under 18 years of age, diagnosis change during the study, and mortality.
ResultsWe inducted a total of 905 patients into this study. We attempted 1:6 nearest neighbor propensity score matching without replacement with a propensity score estimated using logistic regression of the group on age and sex. 41 cases and 96 controls were discarded due to missing values for age and sex. Following matching, 11 more participants from the control group were discarded. Finally, data from 798 cases and 4788 control participants were analyzed. Urinary tract infection rate increased when patients were exposed to Rituximab, Beta1b, Fingolimod, Glatiramer, and Azathioprine (P-value<0.05). Vaginitis incidence was increased when patients were exposed to Fingolimod and Glatiramer Acetate (P-value<0.05). EDSS and MS duration affected the UTI risk (P-value<0.05).
ConclusionMS and the use of DMTs can result in an increased rate of urological infections. Healthcare workers should screen the MS Patients for UTI and vaginitis more often to prevent disease progression or choose the proper treatment regimen.
Keywords: infections, urology, Disease Modifying Therapies, Multiple Sclerosis, Risk Assessment