فهرست مطالب
Jundishapur Journal of Chronic Disease Care
Volume:11 Issue: 3, Jul 2022
- تاریخ انتشار: 1401/05/18
- تعداد عناوین: 10
-
-
Page 1Context
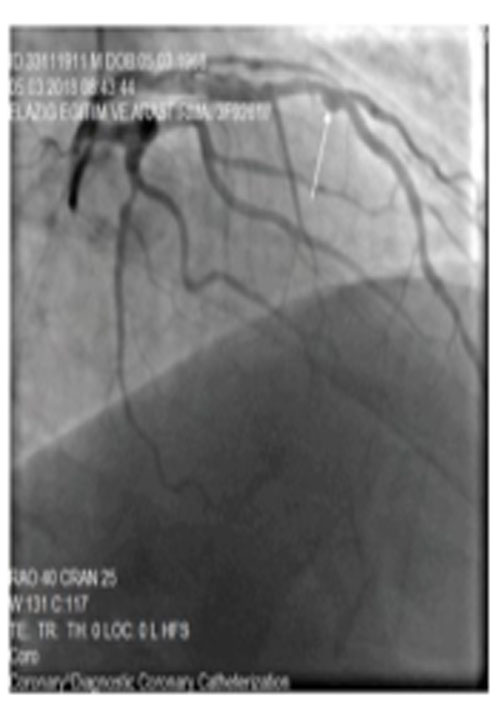
Although the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of coronary artery ectasia (CAE) and its treatment methods are not known for certainty, increased inflammatory and coagulation responses can be responsible for the formation of ectasia due to vascular disorders.
Evidence AcquisitionThe content used in this paper was obtained from English language articles (2005 - 2020) retrieved from the PubMed database and Google scholar search engine using “coronary artery ectasia”, “treatment”, “drug”, and “aneurysm” keywords.
ResultsThe proven effect of inflammation and coagulation in CAE has posed a significant challenge for disease management. Therefore, anti-inflammatory and anticoagulation drugs can be treatment options for these patients. Increased inflammatory responses and some coagulation factors in CAE patients is undeniable. The study of these two systems in CAE patients and the evaluation of drugs affecting these mechanisms to achieve a definitive conclusion requires further and more extensive studies.
ConclusionsWe evaluated the hypothesis that anti-inflammatory and anticoagulation drugs with improved vascular endothelial function may accelerate the healing process of CAE patients; thus, they may be treatment options. Finally, it can be said that identifying molecular pathways related to drugs can improve their effectiveness in treating patients and increasing their survival. In addition, identifying upstream and downstream pathways can help diagnose the disease pathogenesis in addition to treating patients.
Keywords: Aneurysm, Coagulation, Coronary Artery Ectasia, Drug, Inflammation -
Page 2Background
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are among the most important compounds that cause adverse health outcomes in humans, such as poor lung function, bronchitis, asthma, shortness of breath, circulatory disorders, lung cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and mortality.
ObjectivesThis review aims to investigate the effects of PAHs on the occurrence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
MethodsA narrative review of the literature was done from 1979 to 2021 in various databases: Science Direct, PubMed, Web of Science, Springer, and Google Scholar. We found 76 and 14 articles by searching the databases and other sources, respectively. Twelve articles were included after screening. The literature indicates the significant adverse effect of PAHs on the occurrence of COPD.
ResultsHeavy industries (oil, steel, gas, and petroleum) are the primary sources of PAHs. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons induce respiratory diseases, as they are destructive to the lung, leading to COPD. Sex, age, nutritional status, health, duration of exposure to PAHs, and body response to the pollutants affect the complications.
ConclusionsHigh PAH levels can increase the risk of COPD, respiratory diseases, and incremental lifetime cancer risk (ILCR).
Keywords: Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Health Effect, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary, Cancer -
Page 3Background
The news of several people being affected by unusual pneumonia at the beginning of the year 2020 in China led to the introduction of a new type of coronavirus as the cause of a new respiratory disease. With the rapid spread of the disease in China and then to other parts of the world, the new coronavirus became scientifically known as severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the resulting disease as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This disease has a variety of symptoms and can cause SARS.
ObjectivesThis study aimed to investigate the chronic diseases affecting the mortality rate of this disease.
MethodsThis retrospective cohort study was performed on 7222 eligible patients admitted to hospitals in Sirjan, Iran, from March 2020 to June 2021 with a positive polymerase chain reaction for COVID-19. The researcher extracted information from the patients’ files using the questionnaire of demographic characteristics, clinical signs and symptoms, and the history of underlying diseases. The data were analyzed by the SPSS software using descriptive and analytical statistical tests, namely chi-squared, independent samples t-test, and univariate and multivariate logistic regression tests.
ResultsOut of 7,222 patients with COVID-19, 294 died, of whom 152 weremale and 142 were female (OR = 1.23, CI: 0.97 - 1.55). Moreover, 220 people out of 294 dead cases were over 60 years old (OR = 8.92, CI: 6.82 - 11.67). The most common diseases were hypertension (OR = 3.63, CI: 2.81 - 4.69) and diabetes (OR = 3.16, CI: 2.38 - 4.20). The most common symptoms among those who died were respiratory distress (51.4%) and cough (34.7%).
ConclusionsThemortality rate is directly related to the underlying diseases in COVID-19, and themost common underlying disease in the statistical population of this study was hypertension. In addition, respiratory distress is a common symptom in dead patients, which can be used as a predictor of death.
Keywords: COVID-19, Chronic Disease, Mortality -
Page 4Background
Nowadays, many patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) experience the final stage of the disease, ie, ESKD. Dialysis and kidney transplantation are considered the usual treatment for this stage of the disease, among which kidney transplantation is the best treatment. Some patient needs a second transplant since this treatment is not always successful.
ObjectivesThis study was done to evaluate the survival rates between the two kidney recipient groups (first and second transplants).
MethodsThe sample included all the first and second kidney transplant patients referred to the transplant center of Imam Khomeini Hospital in Urmia from 1991 to 2016. This study was considered the retrospective cohort analysis. Data were analyzed using SPSS software version 18 after completing the checklists.
ResultsA total of 245 people entered the study based on the inclusion criteria. The overall survival of the patients was 128.27 ± 294.29 months. The average age of the second transplant patients was higher compared to that of the first, and this difference was not statistically significant.
ConclusionsIn general, the results indicated that the patients with the first transplant have longer survival than the secondary can be reduced when the patients at risk are identified and treated.
Keywords: Kidney Transplantation, Kidney Function Test, Chronic Kidney Failure -
Page 5Background
Today, cancer is one of the leading public health concerns worldwide. Being diagnosed with cancer is not necessarily a life-threatening event for children and their families.
ObjectivesIn this view, this study was done to determine the impact of family empowerment programs on the knowledge and care performance of mothers with leukemia children.
MethodsThe present study is a randomized clinical trial conducted on 62 mothers of children with cancer who were referred to the oncology wards of some educational hospitals in Ahvaz. The subjects were randomly divided into two intervention and control groups. The education was conducted in five sessions of 45 minutes (two sessions per week).
ResultsComparison of the mean score of the knowledge of mothers of children with leukemia before education (3.09) and after education (6.29) was one of the interventions that were significant in the intervention group (P < 0.001), but in the control group, no significant statistical difference was observed.
ConclusionsThe results of the study indicated that by educating the family through the family-centered empowerment model, it is possible to increase the caregiving knowledge of mothers and prevent chemotherapy complications in children
Keywords: Leukemia, Family-Centered, Empowerment, Knowledge, Care, Children -
Page 6Background
Today, the construct of well-being has influenced the field of education. In this regard, one of the important educational objectives in advanced societies is to provide psychological well-being for students. Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is considered as one of the most common mental disorders affecting all aspects of life with destructive effects in the long run on interpersonal and social relationships.
ObjectivesThis study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of positivity on academic well-being in students with OCD.
MethodsThe population of this quasi-experimental study included all female students studying in secondary schools in Zahedan during the academic year 2020 - 2021. Using convenience sampling method, a total of 30 participants diagnosed with OCD were assigned into two equal groups of experimental and control (n = 15 in each). The experimental group received positivity training for eight sessions (each session 60 minutes). For data collection, Maudsley Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory (MOCI) and Academic Well-Being Scale by Tuominen-Soini et al. were used. The data obtained from pre-test and post-test were analyzed by multivariate analysis of covariance (MANOVA).
ResultsThe results of covariance showed that after training positivity, a significant difference was found between the mean scores of the control and experimental groups in the components of value of school, school burnout, academic satisfaction, involvement in school assignments, and academic well-being (P < 0.05). The difference in post-test scores related to the effect of positivity education according to ETA coefficients in the variables of school value, school burnout, academic satisfaction, school work integration, and academic well-being were 0.86, 0.52, 0.64, 0.77, and 0.81%, respectively.
ConclusionsConsidering the effectiveness of positivity training to promote the dimensions of academic well-being, practitioners are advised to use this kind of training to improve academic well-being of students with OCD.
Keywords: Positivity, Academic well-being, Students, Obsessivee-Compulsive Disorder -
Page 7Background
Disease management approach is an effective means in genetic disorders, such as sickle cell disease (SCD). This disease is a neglected chronic disease of increasing global health importance. In this process, acquiring knowledge and information related to the disease plays a critical role in self-efficacy and self-care. Therefore, one of the determinants of health and criteria for enhanced quality of life is health literacy.
ObjectivesTherefore, the present study aimed to determine the relationship between the quality of life and health literacy associated with disease management among patients with SCD.
MethodsThis descriptive-correlational study was conducted on 150 patients with SCD in Ahvaz. These patients have been referred to the thalassemia clinic and the thalassemia ward of Shahid Baghaei-2 Hospital and selected via accessible sampling. The study data were collected using WHOQOL-EREF-26 items and a researcher-made questionnaire about information resources whose reliability and validity were confirmed. Then, the data were entered into the SPSS software and analyzed via descriptive statistics, chi-square, regression, and correlation tests.
ResultsThe mean age of the participants was 27.56 ± 9.14 years. The most important resource for increasing knowledge was the physician in 83.3% of the patients. In addition, they had acquired the highest amount of knowledge about the causes and symptoms of the disease. Moreover, the highest and lowest mean scores of quality of life were related to physical health (50.80 ± 9.94) and (45.23 ± 19.91) social health dimensions, respectively. The results showed statistically significant differences between the place of residence with the dimension of social health (P = 0.037, b = -11.05) and sources of knowledge enhancement with the dimension of social health quality of life (P = 0.010, b = -14.96).
ConclusionsSince quality of life is a subjective and multifactorial concept, its effective factors have to be explored. The present study results indicated that the patients were eager to acquire knowledge about their disease. The higher the patients’ knowledge level, the higher their ability in disease management, self-care, and social health dimension of quality of life would be.
Keywords: Sickle Cell, Quality of Life, Self-Care, Health Literacy -
Page 8Background
The role of vitamin D deficiency and inflammation levels in renal anemia is well established. However, few studies with inconsistent findings have examined the relationship between vitamin D supplementation and the prevalence and severity of anemia in the chronic kidney disease.
ObjectivesThe present study aimed to evaluate the effect of vitamin D deficiency treatment on hemoglobin levels in hemodialysis patients.
MethodsThe present study was a double-blind, randomized controlled trial on 60 hemodialysis patients aged 18 - 83 years, who were undergoing weekly dialysis and receiving erythropoietin. These patients with vitamin D (< 30 ng/mL) referred to the dialysis wards of Imam Khomeini, Razi, and Sina hospitals in Ahvaz in 2019 and were assigned into two groups. One group was treated with 500 mg oral calcium-D tablets three times a day, and another group was treated with 50,000 units of D-Pearls weekly. The two groups were treated for 12 weeks. Then they were re-evaluated in terms of response to treatment and the rate of improvement in hemoglobin levels and erythropoietin dose.
ResultsIn each intervention group, vitamin D levels increased significantly (P < 0.001). D-Pearls improved vitamin D deficiency; however, the difference was not statistically significant. This study also showed a significant increase in hemoglobin (> 1 unit) in the Calcium-D group; however, such a change was not observed in the D-Pearls group (P = 0.3824). Moreover, there was no difference between the two groups in terms of erythropoietin consumption (P = 0.98), blood calcium level (P = 0.57), parathyroid level (P = 0.20), and phosphorus (P = 0.99).
ConclusionsDespite its significant limitations, this study revealed vitamin D supplements compensated for vitamin D deficiency, and Calcium-D tablets could improve hemoglobin levels in patients.
Keywords: Vitamin D Deficiency, Hemoglobin, Hemodialysis, Erythropoietin, End-stage Renal Disease -
Page 9Background
Sleep quality is a major factor affecting physical and mental health. Poor sleep quality is a common complaint in many psychiatric disorders.
ObjectivesThe present study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), and pharmacotherapy on the sleep quality of women with chronic pain in Tehran, Iran.
MethodsThis randomized clinical trial with a pre-test, post-test, and follow-up design and a control group was performed on the statistical population of all women with chronic pain visiting Pardis Pain Clinic, Tehran, Iran, in 2020. The sample consisted of 60 women with chronic pain. We randomly divided the participants into four groups ACT, pharmacotherapy, tDCS, and control (N = 15 per group). The research instrument was the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI). The data were analyzed using repeated measures analysis of variance by the SPSS software.
ResultsThe participants aged 46.67±8.39, 48.24±7.54, 47.67±7.42, and 47.39±6.85 years in the ACT, pharmacotherapy, tDCS, and control groups, respectively. ACT (F = 7.76, P < 0.001), pharmacotherapy (F = 17.97, P < 0.001), and tDCS (F = 9.37, P < 0.001) significantly improved the sleep quality of patients with chronic pain compared to the control group. The effects of ACT, pharmacotherapy, and tDCS on the sleep quality of women with chronic pain did not significantly differ (P > 0.05).
ConclusionsACT and tDCS intervention programs effectively improved the sleep quality of patients with chronic pain. Therefore, ACT and tDCS are recommended to enhance sleep quality in chronic pain patients.
Keywords: Acceptance, Commitment Therapy, Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation, Pharmacotherapy, Sleep Quality, Chronic Pain -
Page 10Background
Problems with balance and controlling the body’s position are the most common challenges experienced by patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) who experience a high rate of falls.
ObjectivesThe present study aimed to investigate the relationship between the severity and fear of falling (FOF) mediated by disability in patients with MS.
MethodsThis was a correlational study based on structural equation modeling (SEM). The statistical population consisted of all patients with MS who visited the neurology centers of hospitals in Sari, Iran, of whom 200 cases were selected as the sample using convenience sampling. The research instruments included the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I), MS Severity Scale, and the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). The data were analyzed using SEM by SPSS AMOS 25.
ResultsThe participants included 200 patients with MS aged 33.67 ± 6.42 years. In addition, 41.5% were male, and 58.5% of female. The results of SEM indicated that the proposedmodel had a good fit. There was a direct and positive relationship between the severity of MS and FOF (β = 0.69; P = 0.002). Moreover, there was a direct relationship between disability and FOF (β = 0.71; P = 0.011), and between the severity of MS and disability (β = 0.63; P = 0.001) in patients with MS. The findings confirmed the relationship between the severity of MS and FOF mediated by disability in patients with MS (P < 0.001).
ConclusionsBased on the results, FOF wasmarkedly higher in patients with severerMS. Due to the consequences of FOF, counseling training programs should be offered to patients with MS who visit medical centers to improve their health and level of activity and mitigate their FOF.
Keywords: Accidental Falls, Patient Acuity, Disability, Multiple Sclerosis

