فهرست مطالب
فصلنامه نفس
سال یکم شماره 2 (تابستان 1393)
- تاریخ انتشار: 1393/05/11
- تعداد عناوین: 8
-
-
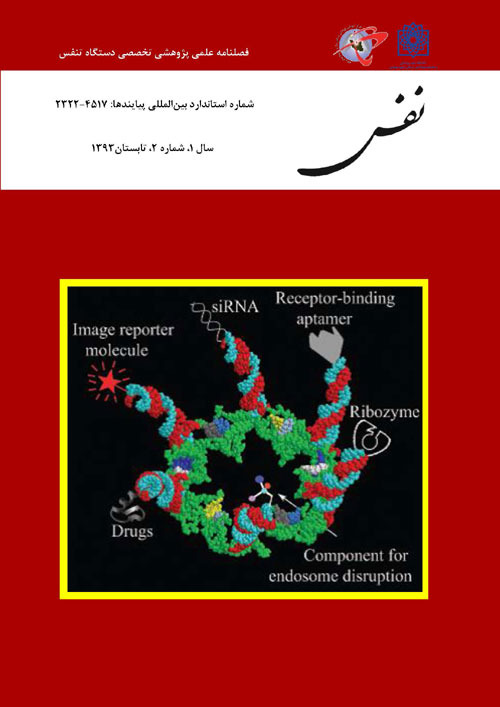
صفحات 1-9ماکرومولکول های زیستی اعم از RNA، DNA و پروتئین ها به دلیل دارا بودن پتانسیل های ذاتی ویژه، به عنوان واحدهای ساختاری برای تهیه نانوابزارها، بکار گرفته می شوند. پروتئین ها در نانوزیست فناوری بصورت گسترده مورد استفاده قرار گرفته اند و نانوفناوری DNA نیز از جوانب بسیاری مطالعه شده است. اما مفهوم نانوفناوری RNA اخیرا مطرح گردیده است و اولین شواهد مبنی بر ساخت نانوذرات RNA از طریق فرایند خودساماندهی چندین مولکول RNA طبیعی یا مهندسی شده، در سال 1998 مطرح شد. از آنجایی که مولکول های RNA به مانند DNA به سهولت قابل دست ورزی بوده و مثل پروتئین ها دارای تنوع بسیار در ساختار و عملکرد خود هستند، در نانوزیست فناوری بسیار مورد توجه واقع شده اند. نانوذرات RNA طی فرایند خودسامانده و با استفاده از میانکنش های هماهنگ، بین مولکول های RNA گرد هم می آیند و ساختارهای دو یا سه بعدی را ایجاد می کنند. اولین و بهترین RNA با کاربرد نانوفناوری که تاکنون شناخته شده، موتور packing RNA باکتریوفاژ 29φ است که قابلیت ایجاد دیمر، تریمر و هگزامر را داراست. به این نانوذرات، می توان مولکول های درمانی، تشخیصی و گیرنده ها، اعم از siRNA ها، ریبوزیم ها و آپتامرهای RNA را متصل نمود. از جمله عوامل درمانی قابل استفاده، siRNAهای طراحی شده علیه سرطان ریه است. در این سرطان، بافت بدخیم در یک یا هر دو ریه رشد می کند. سرطان ریه یکی از همه گیرترین سرطان ها در سراسر جهان است و بیش از 80% بیماران در کمتر از 5 سال از زمان شناسایی بیماری، جان خود را از دست می دهند. از بین همه siRNAهای مورد استفاده برای درمان سرطان ریه، siRNAهای ژن های KRAS و P53 تاثیر بیشتری در بهبودی این بیماری نشان داده اند. در این مقاله، مفاهیم مربوط به ساختار و عملکرد RNAهای مورد استفاده در نانوزیست فناوری، رویکردهای مورد استفاده به منظور مهندسی یا ساخت این RNAها و تبدیل آنها به نانوذرات کاربردی مرور گشته و نقش آنها در درمان سرطان ریه بررسی شده است.
کلیدواژگان: سرطان ریه، نانوفناوری RNA، خودسامان دهی، مولکول های RNA درمانی -
صفحات 10-18بیماری سل به عنوان یکی از بیماری های تاثیرگذار بر روی سلامت و بهداشت جهانی شناخته می شود. فهم شیوه انتقال و شیوع و بررسی فاکتورهای میزبان و همچنین خصوصیات و فاکتورهای باکتری مایکوباکتریوم توبرکلوزیس که می توانند در شیوع بیماری سل تاثیر داشته باشند برای مدیریت شیوع و کنترل و مبارزه با این بیماری بسیار حیاتی می باشد. در همین راستا و برای به دست آوردن این اطلاعات استفاده از تکنیک های مولکولی و روش های اپیدمیولوژی بسیار ضروری هستند. یکی از روش هایی که امروزه مورد مطالعات بسیار قرار گرفته، بررسی مناطق ژنی موسوم به ناحیه تفاوت (RD) می باشد که در این مطالعه به بررسی این مناطق می پردازیم.
ابتدا 190 سویه مایکوباکتریوم توبرکلوزیس با روش های اسپولیگوتایپینگ شناسایی شدند. مقاومت دارویی این سویه ها مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. در نهایت 6 لوکوس RD مورد نظر از جنبه حذف (Deletion) در ژنوم این 190 سویه با روش PCR مورد بررسی و آنالیز قرار گرفتند.
از سویه های مایکوباکتریوم توبرکلوزیس با روش اسپولیگوتایپینگ،(H4(127 در72 نمونه (5/ 37%)، CAS در 37 مورد (20%)،T1 در 18 نمونه (5/ 9%) و Beijing در 11 مورد شناسایی شدند و باقی نمونه ها شامل 52 مورد (27%) ناشناخته بودند. 70% نمونه ها حساس به دارو و 30% مقاوم بودند. در سویه های Beijing، لوکوسهای RD181 و RD105 و در سویه BCG لوکوسRD1، حذف داشتند.
بررسی مناطق RD روشی ساده و سریع است. استفاده از RD1 جهت شناسایی سویه BCG و همچنین RD181 جهت شناسایی سویه Beijing مناسب می باشد اما RD150 به علت عدم وجود پلی مورفیسم در سویه های مختلف کارایی چندانی به عنوان یک روش اپیدمیولوژی ندارند. همچنین در این تحقیق مشخص شد که مقاومت دارویی ارتباطی با حذف در مناطق RD ندارد.
کلیدواژگان: اپیدمیولوژی ملکولی، سل، اسپولیگوتایپینگ، ناحیه تفاوت -
بررسی ارتباط میان مصرف دخانیات و مصرف مواد مخدر: آیا مصرف دخانیات دروازه ورود به مصرف مواد مخدر است؟صفحات 19-24مصرف مواد مخدر یکی از بزرگ ترین معضلات فرهنگی، اجتماعی و بهداشتی در عصر حاضر قلمداد می شود. کنترل و کاهش عوامل موثر در رو آوردن به مصرف مواد مهم ترین اقدامی است که می تواند در سلامت آینده جامعه نقش داشته باشد. این مطالعه در راستای بررسی میزان تاثیر مصرف دخانیات در گرایش به مواد مخدر طراحی و اجرا شده است.
در این مطالعه مقطعی 1372 پرونده مراجعه کنندگان برای ترک مواد مخدر از لحاظ وضعیت مصرف دخانیات و سایر فاکتور های مرتبط مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. یافته ها مورد تجزیه و تحلیل آماری قرار گرفت.
1306 مرد (2/ 95%) و 66 زن (8/ 4%) مورد بررسی قرار گرفتند. بیش از 90% افراد مراجعه کننده در زمان مراجعه سیگاری بودند. بیشترین شروع مصرف دخانیات در این گروه 16 تا 20 سال بود. میانگین سن شروع مصرف دخانیات 6/ 5 ± 2/ 19 با نمای 18 سال و میانگین سن شروع مصرف مواد مخدر 1/ 7 ± 3/ 21 با نمای 20 سال گزارش شد. میان سن شروع مصرف دخانیات و شروع مصرف مواد مخدر ارتباط معنی داری وجود داشت.
مصرف دخانیات می تواند بهعنوان یک عامل زمینه ساز در جهت اعتیاد به مواد مخدر شناخته شود. این امر لزوم اجرای صحیح و دقیق قوانین کنترل دخانیات و اقدامات پیش گیرانه و ضرورت ترک مصرف دخانیات در سنین پایین را یادآور می نماید.
کلیدواژگان: دخانیات، مواد مخدر، گرایش به مصرف -
صفحات 25-33نگرش مردم به ویژه اقشار آموزش پذیر در خصوص راهکارهای مقابله با آلودگی هوا عامل تعیین کننده مهمی برای تدوین برنامه های آموزشی در مورد روش های کاهش آلودگی هوا می باشد. این مطالعه با هدف یاری مسئولین در امر برنامه ریزی های آموزشی، به بررسی نگرش دانش آموزان شهر تهران در مورد راهکارهای مقابله با آلودگی هوا می پردازد. در این پژوهش مقطعی به روش نمونه گیری چندمرحله ای، از یک پرسشنامه با سوالات بسته، به منظور تعیین نگرش 2140 دانش آموز مدارس راهنمایی و دبیرستان تهران در مورد راهکارهای کاهش آلودگی هوا و برداشتی که از میزان آگاهی خود دارند و میزان درک خطر ایشان در خصوص آلودگی هوا استفاده شد. از آزمون های آماری Chi Square، Mann-Whitney، Kruskal-Wallis برای تحلیل داده ها استفاده شد. درحالیکه دامنه امتیاز پاسخ هیجانی (Affective score) از 12- تا 12+ متغیر بود، میانگین به دست آمده برابر با 76/ 5 (انحراف معیار: 79/ 3) بود (دختران 43 /5 و پسران 94/ 5، با اختلاف آماری معنی دار). از بین راهکارهای پیشنهادی برای مقابله با آلودگی هوا دانش آموزان با راهکار «من و دوستانم باید بیشتر درباره آلودگی هوا آموزش ببینیم» بیش از سایر راهکارها موافق بودند. در نتیجه می توان گفت دانش آموزان در مورد مسئله آلودگی هوا بسیار ابراز نگرانی می کنند و به عبارتی درک مناسبی از خطر دارند ولی به نظر می رسد اقدامات انجام شده در جهت کاهش معضل آلودگی هوا از نظر دانش آموزان قابل قبول نبوده است. از این رو ضروری است که با برنامه ریزی های جامع تر و اجرای دقیق آن ها، پاسخگوی انگیزه بالای دانش آموزان جهت مقابله با آلودگی هوا باشیم.
کلیدواژگان: آلودگی هوا، دانش آموزان، راهکار، نگرش -
صفحات 34-40ریزRNAها یا miRNAها نقش مهمی در سرطان زایی از جمله در سرطان ریه دارند. همچنین جهش های مرتبط با ژن TrkC در سرطان ریه گزارش شده است. به تازگی در دانشگاه تربیت مدرس یک ریزRNAی جدید مستقردر ژن TrkC انسانی کشف گردیده و با شماره دسترسی HG969187 در پایگاه اطلاعاتی EBI به ثبت رسیده است. هدف از مطالعه حاضر بررسی بیان این ریزRNA، با نام TrkC-miR1، در نمونه های سرطانی و سالم بافت ریه انسان می باشد. از 11 بیمار مبتلا به سرطان ریه نمونه های سرطانی و سالم بافت ریه تهیه و استخراج RNA صورت گرفت. پس از سنتز cDNA از تمام نمونه ها، بیان TrkC-miR1 با استفاده از روش real-time PCR سنجیده شد. تحلیل داده ها حاکی از آن است که بیان TrkC-miR1 در نمونه های اسکواموس سل کارسینوما نسبت به بافت سالم حاشیه توموری در همان افراد افزایش یافته است، درحالیکه بیان آن در نمونه های لارج سل کارسینوما و آدنوکارسینوما نسبت به بافت سالم حاشیه توموری در همان افراد کاهش یافته است. نتایج این تحقیق نشان می دهد که TrkC-miR1 در نمونه های هیستوپاتولوژی مختلف سرطان ریه بیان متمایزی دارد. به نظر می رسد با بررسی بیان TrkC-miR1 در تعداد نمونه های توموری بیشتر می توان به یک مارکر تشخیصی برای بافت های سرطانی مختلف ریه دست یافت.
کلیدواژگان: سرطان ریه، ریزRNA، TrkC -
صفحات 41-47الگوی تنفس از لحاظ تغییرپذیری فرکتالی در بیماران تنفسی از جمله آسم بررسی نشده است. هدف از این مطالعه آنالیز الگوی تنفس افراد سالم و بیماران مبتلا به آسم از لحاظ تغییرپذیری فرکتالی است. این مطالعه بر روی 40 فرد مذکر (10 نفر افراد سالم، 10 نفر آسم آتوپیک کنترل شده، 10 نفر آسم آتوپیک کنترل نشده، 10 نفر آسم غیرآتوپیک کنترل نشده) در بیمارستان مسیح دانشوری انجام شد. تغییرات قفسه سینه و شکم در حین تنفس توسط دو کمربند تنفسی جمع آوری و به حجم تنفسی کالیبره شدند. ساختار فرکتالی تغییرات فواصل بین تنفس و حجم تنفس با روش (Detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA آنالیز شد. در بررسی فواصل بین تنفس (IBI)، مقدار شاخص α در گروه های افراد سالم، آسم آتوپیک کنترل شده، آسم آتوپیک کنترل نشده و آسم غیرآتوپیک کنترل نشده به ترتیب برابر 03/ 0±82/ 0، 06 /0±73/ 0، 04/ 0±68/ 0 و 0/04±0/57و در بررسی تغییرات حجم تنفس به ترتیب معادل 10/ 0±83/ 0، 06 /0±75/ 0، 05/ 0±70/ 0 و 04/ 0±59/ 0 محاسبه گردید. اختلاف معناداری در شاخص α بین گروه های مختلف، از نظر تغییرات فواصل بین تنفس و تغییرات حجم تنفسی مشاهده شد (P<0.05). در مجموع چنین نتیجه گیری گردید که الگوی تنفس بیماران مبتلا به آسم دارای همبستگی فرکتالی کمتر نسبت به افراد سالم است. در شرایط آسم کنترل نشده این اختلاف افزایش می یابد.
کلیدواژگان: آسم، الگوی تنفس، تغییرپذیری فرکتالی -
صفحات 48-53مساله اهدای عضو در دنیا روز به روز از اهمیت بیشتری برخوردار می گردد. آگاهی و نگرش نسبت به این موضوع از جانب کادر درمانی، بویژه پرستاران، مورد توجه بوده و انگیزه مثبت در این گروه می تواند در رسیدن به این هدف بسیار کمک کننده باشد. هدف این مطالعه بررسی نگرش، آگاهی و عملکرد پرسنل پرستاری نسبت به پیوند اعضا در بیمارستان دکتر مسیح دانشوری می باشد.
این مطالعه از نوع توصیفی بوده و نظرات 66 نفر از پرستاران شاغل در بخش های مختلف بیمارستان که دارای حداقل یک سال سابقه کار در این بیمارستان بوده اند را مورد بررسی قرار داده است. انتخاب افراد به روش نمونه گیری تصادفی بود. نگرش، آگاهی و عملکرد پرستاران به وسیله پرسشنامه مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. پرسشنامه شامل اطلاعات دموگرافیک و سوالات مربوط به نگرش، آگاهی و عملکرد پرستاران نسبت به پیوند اعضا بوده است که اعتبار آن به وسیله اعتبار محتوا و پایایی آن به وسیله آزمون مجدد تعیین گردید. نتایج با کمک نرم افزار آماری (Ver. 16) SPSS و از طریق آزمون های آماری و آمار توصیفی شامل جداول توزیع فراوانی مطلق، نسبی و میانگین و انحراف معیار مورد بررسی قرار گرفت.
اکثریت افراد مورد پژوهش در محدوده سنی 20 تا40 سال (2/ 74% زن و 8/ 25% مرد) بودند. نتایج نشان داد بین سن پرستاران و تاثیر مسائل روحی و روانی در روند کاری مراقبت از بیمار مرگ مغزی رابطه معکوس و معنی داری وجود دارد. همچنین نتایج نشان داد که دیدگاه 3/ 12% از پرستاران مورد مطالعه در خصوص پیوند اعضاء مخالف، 6/ 17% کاملا موافق، 7/ 54% موافق مبنی بر بهبود شرایط و 4/ 15% بی تفاوت بوده اند. 4/ 92% در این مطالعه هیچ دوره آموزشی را در مورد پیوند نگذرانده بودند.
نتایج بدست آمده نشان می دهد که درصد بیشتری از پرستاران دارای عدم آگاهی نسبت به پیوند اعضاء بوده و از آنجایی که گذراندن دوره های آموزشی و ایجاد آگاهی می تواند به میزان بالایی در نگرش مثبت آنها موثر باشد، بنابراین افزایش آگاهی پرستاران در کنار بهبود شرایط می تواند در جهت بهبود مراقبت از بیمار پیوندی حائز اهمیت گردد.
کلیدواژگان: پیوند اعضا، پرستار، آگاهی و نگرش، بیمارستان -
صفحات 54-58در بیماران مبتلا به میاستنی گراو بیهوشی برای جراحی رزکسیون آناستوموز نای چالشی پیچیده است. علت اساسی این چالش این است که بسیاری از این بیماران ممکن است در مرحله ی پس از عمل تا مدتی نیاز به ادامه ی لوله گذاری و تهویه ی مکانیکی ریه ها داشته باشند. از سویی دیگر نیز فشار مثبت راه هوایی و فشار کاف لوله نای با خطر گسست محل آناستوموز در نای همراه است. در اینجا استفاده از روش بیهوشی کامل وریدی، بدون شل کننده عضلانی جهت رزکسیون و آناستوموز تراشه برای درمان تنگی ساب گلوت به دنبال لوله گذاری طولانی، در یک بیمار میاستنی گراو را معرفی می کنیم.
کلیدواژگان: میاستنی گراو، بیهوشی داخل وریدی، جراحی، پروپوفول، رمیفنتانیل، تنگی نای
-
Pages 1-9Biological macromolecules, including DNA, RNA, and proteins, have intrinsic features that make them potential building blocks for the fabrication of nanodevices. Peptides and proteins have been studied for applications in nanotechnology extendedly and the field of DNA nanotechnology is now well established. The concept of RNA nanotechnology has been around for more than a decade, and the first evidence for the construction of RNA nanoparticles through the self-assembly of several re-engineered natural RNA molecules reported in 1998. Since RNA molecules can be designed and manipulated with both a level of simplicity characteristic of DNA and a versatile flexibility in structure and function (including enzymatic activities) similar to that of proteins, there became an interesting candidate for nanotechnological applications. Two and three dimensional structure of RNA nanoparticles can be fabricated by self-assembled interactions of special RNA molecules. The best characterized RNA multiplier and the first to be described in the RNA nanotechnological application is the motor pRNA of bacteriophage phi29 which form dimers, trimers, and hexamers. Both ribozyme or therapeutic siRNA and a receptor binding RNA aptamer have been engineered into individual RNA nanoparticles. The most important disease that needs the help of RNA nanotechnology to improve the degree of malignancy is lung cancer. Lung cancer is one of the widespread cancers all over the word and the patients often died after 5 years of challenging with this disease. Among all siRNAs applied for lung cancer therapy KRAS and P53 siRNAs are most important one on. This review covers the basic concepts of RNA nanoparticles structure and their role in lung cancer therapy.Keywords: Lung Cancer, RNA Nanotechnology, Self-Assembly, Therapeutic RNAs
-
Pages 10-18Tuberculosis epidemiology is valuable for control of TB by understanding the transmission dynamics. A potential molecular epidemiology method to distinguish the origins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is region of differences (RDs) polymorphisms. Worldwide, 68 RDs have been specified, so far. By studying deletion and polymorphisms in the RD regions of RD1, RD150 and RD181, this study focused on the molecular diversity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Iran for the first time. One hundred ninety Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains were isolated from patient’s clinical samples in Mycobacteriology Research Center (MRC). DNA was extracted and spoligotyping was performed by using DR region PCR. The spoligotyping patterns were obtained from SPOLDB4 database. Drug susceptibility tests were performed for all isolates and finally, three regions of RD1, RD150 and RD181 loci were amplified by PCR. Out of 190 M. Tuberculosis strains, 70% of isolates were susceptible to Isoniazid, Rifampin and Etambutol drugs and the remaining (30%) were drug resistant. The spoligotyping patterns demonstrated H4 (127) and CAS families were more prevalent than other families by 37.5% and 20% respectively. Other prevalent families were T1 (9.5%), Beijing (11%) and unknown families (27%). The RD181 loci had deletion in Beijing strains, and RD1 showed deletion in BCG strains. The RD150 loci showed deletion in none of the strains. The RD1 and RD181 are appropriate to identify BCG and Beijing strains respectively. Whereas, RD150 loci is not efficient to show polymorphisms in various strains. As a result RD1 and RD181 polymorphism detection can be used effectively for molecular epidemiology studies to determine ongoing transmission clusters.Keywords: Molecular Epidemiology, Tuberculosis, Region of Difference, Spoligotyping
-
Pages 19-24Substance abuse is among the biggest cultural, social and health dilemmas in the current world. Control and reduction of factors that enhance substance abuse may be helpful in this respect. This study evaluated the effect of tobacco smoking on the tendency to substance abuse.In this cross-sectional study, 1,372 records of clients presenting for substance abuse treatment were evaluated in terms of tobacco smoking status and other related factors. Data were statistically analyzed.A total of 1,306 males (95.2%) and 66 (4.8%) females were evaluated. More than 90% of participants were tobacco smokers. The highest frequency of smoking initiation was in the age group of 16-20 yrs. The mean age of smoking onset was 19.2±5.6 years with a mode of 18 years. Meanwhile, the mean age of substance abuse onset was 21.3± 7.1 years with a mode of 20 years. A significant association between the initiation age of smoking and substance abuse onset were found.Tobacco smoking can be a predisposing factor for substance abuse. This association necessitates the precise implementation of tobacco control policies and preventive measures and emphasizes on smoking cessation at early ages.Keywords: Tobacco Use, Illicit Drugs, Tendency to Substance Abuse
-
Pages 25-33People’s attitude towards combating air pollution is an important determining factor in creating an appropriate base for providing educational programs about air pollution reduction. This study examines school student's attitudes towards ways of combating air pollution in order to assist authorities in educational planning.In this cross-sectional study, a closed-form questionnaire was used to evaluate 2140 guidance and high school student's attitude towards ways of air pollution reduction, their idea about their own knowledge on this subject and also their risk perception about air pollution. Some statistic tests such as Chi Square, Mann-Whitney, Kruskal-Wallis were used to analyze data. The sampling method was multi stage.While the range of student’s ‘affective score’ varied from -12 to +12, student's mean affective score was equal to +5.76 (SD 3.79). Affective Score was significantly different between girls and boys (5.43 vs. 5.94 respectively). Among the suggested ways of combating air pollution, they agreed with "Me and my friends should be taught more about air pollution" more than other ways.The students worried so much about air pollution and they had appropriate risk perception about it, however, it seems the actions that have been done in this regard were not acceptable by them. Hence, it is essential to respond to their high motivation by more comprehensive planning and precise administrative methods.Keywords: Reducing Air Pollution, Students, Attitude
-
Pages 34-40MicroRNAs play pivotal role in tumorigenesis, including lung tumors. Mutations of TrkC gene are also related to lung cancers. Recently, we have discovered a novel miRNA named TrKC-miR1 (has-miR11181), located in the human TrKC gene (EBI acc # HG969187). Here, we intended to investigate TrKC-miR1 expression status in pairs of lung tumors and their marginal tissues.Total RNAs from 11 lung tumors and their marginal tissue samples were extracted. Then, real-time PCR was performed to analyze TrkC-miR1 expression, following cDNA synthesis.Data analysis revealed that TrkC-miR1 expression was elevated in squamous cell carcinoma related to marginal tumor tissues. However, TrkC-miR1 expression was decreased in large cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, compared to the marginal tumor tissues.Results of current study shows that TrkC-miR1 has a distinct expression pattern in different histopathological types of lung tumor. It remains to be tested in more tumor samples, if TrkC-miR1could be used as a tumor marker for distinction of lung tumor subtypes.Keywords: Lung tumor, TrkC-miR1, TrkC
-
Pages 41-47There is no study about fractal variability of breathing pattern in patients with respiratory diseases, such as asthma. The aim of this study was evaluating fractal variability of breathing pattern in healthy and asthmatic cases. Forty men, including 10 healthy volunteers, 10 patients with controlled atopic asthma (CAA), 10 patients with uncontrolled atopic asthma (UAA), and 10 patients with uncontrolled non-atopic asthma (UNAA) referred to the outpatient clinic of Dr. Masih Daneshvari Hospital (Tehran, Iran) were enrolled in this study. The thoraco-abdominal movements were collected using two respiratory belts and then signals were calibrated to respiratory volume. We analyzed the fractal variability of inter breath interval (IBI) and volume fluctuation using detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA). The α index values in healthy, CAA, UAA, and UNAA cases with respect to IBI were 0.82±0.03, 0.73±0.06, 0.68±0.04, and 0.57±0.04, respectively, and with respect to volume fluctuation were 0.83±0.10, 0.75±0.06, 0.70±0.05, and 0.59±0.04, respectively. There were significant differences between all groups in α index values of both IBI and volume fluctuation (p<0.05). We concluded that the fractal correlation of breathing pattern in asthmatic patients is lower than healthy cases. This difference increased in uncontrolled asthma.Keywords: Asthma, Breathing Pattern, Fractal Variability
-
Pages 48-53The importance of organ donation is increasing world wild. The knowledge and attitude of the medical staffs, including nurses, and their positive motivation in this regard are considered as the advantage to achieve a better transplantation results. This study aimed to investigate nurses’ attitude, awareness and performance about organ transportation in Dr. Masih Daneshvari Hospital. The present study evaluated the opinions of 66 randomly selected, educated nurses who had at least one year experience in different wards of the hospital. Using a Farsi questionnaire, nurses’ attitudes, knowledge and practice data on organ transplantation, as well as their demographic information were surveyed. The validity and reliability of the questionnaire were determined by means of content validity and test-retest (r=0.81) methods, respectively. Using SPSS 16, data analysis was done, hence, descriptive (i.e. absolute and relative frequency tables, mean and standard deviation) and analytical (e.g. Chi2, t-test) statistical results were obtained. The range of age of the majority of participants was 20-40 years old (74.2% woman and 25.8% man). The results showed a significant inverse relationship between the age and the psycho-emotional status of the nurses, regarding the care of brain death patients. The participants’ point of view on the organ transplantation was 12.3% opposite, 17.6% surely agree, 54.7% agree only when there is condition improvement, and 15.4% indifferent.The results also showed that a high percentage of nurses have lack of enough knowledge on organ transplantation. As the educational course and subsequent awareness can be highly effective on their attitude, therefore, the increase of awareness, together with condition improvement, could be important to enhance the care of transplant patients.Keywords: Organ Transplantation, Nurse, Knowledge, Attitude, Hospital
-
Pages 54-58In patients with myasthenia gravis, anesthesia for tracheal resection and reconstruction surgery is a serious challenge; due to post-surgical considerable risk for mechanical ventilatory support. Postoperative positive pressure ventilation and an endotracheal cuff pressure may cause anastomosis dehiscence after surgery.In this case report, we discuss the usage of a non-relaxant, total intravenous anesthesia technique to decrease the risk of post-surgical ventilatory support, in a case of tracheal resection surgery of a myasthenia gravis patient with post intubation subglottic stenosis.Keywords: Myasthenia Gravis, Intravenous Anesthesia, Surgery, Propofol, Remifentanil, Tracheal Stenosis


