فهرست مطالب
Pharmaceutical Sciences
Volume:25 Issue: 3, Sep 2019
- تاریخ انتشار: 1398/07/09
- تعداد عناوین: 13
-
-
Pages 177-183Background
Lidocaine is a well-known medium-acting local anesthetic with a short onset time. It is a valuable drug for managing both acute and chronic pains and is being used as a popular agent for pain control in the emergency department (ED). In this systematic review, we intended to define the effectiveness of lidocaine in pain management of the patients referring to ED.
MethodsThe preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) statement was utilized for this Systematic Review (SR). We searched the databases of PubMed, Scopus, ProQuest, and Medline (Ovid) from 1990 to August 2017 for Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) in which the study population was referred to the emergency department and received lidocaine. Full-texts of the studies that were published in English were reviewed for inclusion. Both authors individualistically evaluated all studies. Seven articles were eligible for the meta-analysis based on their common outcomes.
ResultsThe total number of subjects was 671. The studies were categorized based on the type of drug and administration route. Mean pain, regardless of the drug administration method, in the placebo group was 0.69 units higher than the lidocaine group. Considering the administration route, mean pain in the placebo group was 0.35 units higher than the lidocaine group when administered topically, and it was lower in the subcutaneous method than the topical method by 1.41 units.
ConclusionInfiltration of lidocaine decreases pain of different procedures in the ED whereas the effect of topical lidocaine is controversial issue.
Keywords: Lidocaine, Pain management, Emergency medicine -
Pages 184-189Background
Certain plants stimulate spermatogenesis and increase fertility; in contrast, some plants arrest the spermatogenesis cycle. Ceratonia siliqua is an herb plant with a strong antioxidant property. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of carob fruit extract on spermatogenesis, testicular apoptosis, and oxidative stress in adult male mice.
MethodsForty adult male mice were randomly divided into five groups: control, sham, and carob 1–3. The sham group was injected with normal saline and the carob 1–3 groups were injected with 200, 400, and 800 mg/kg of the carob fruit extract intraperitoneally for 14 days, respectively. At the end of the injection period, spermatogenesis, testicular apoptosis, and oxidative stress were examined.
ResultsThe sperm parameters increased in the mice that received 200 mg/kg of carob compared to the sham group (p <0.05). There was a significant increase in the weight index of the epididymis in the carob 3 group in comparison to the sham group (p = 0.01). The number of positive tunnel cells was not statistically significant between different groups (p>0.05). The level of malondialdehyde decreased in the carob 1 and carob 3 groups, but this reduction was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). In addition, the statistical analysis showed a significant difference in the mean superoxide dismutase levels in the carob 2 and carob 3 groups in comparison to the sham group (p ≤ 0.001). The statistical analysis showed a significant increase in the mean level of the catalase enzyme in the carob 1 group in comparison to the sham (p = 0.02), and carob 2 groups (p = 0.008).
ConclusionThe administration of 200 mg of the carob fruit extract for 14 days increased the testicular index as well as sperm parameters and decreased the level of oxidative stress in the testicular tissue of adult mice.
Keywords: Ceratonia siliqua, Mice, Spermatozoa, Apoptosis -
Pages 190-197Background
Propolis (PRS) and probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus are natural products used as dietary supplement for their therapeutic benefits. This study was performed to examine the possible hepatoprotective effect of PRS and probiotics (PRCs) against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury.
MethodsExperimentally, intoxicated rats received 0.5 ml/kg CCl4 (i.p.) daily for six days, pretreated rats received per os PRS 100 mg/kg or PRCs 109 CFU for six days followed by a single dose of 0.5 ml/kg CCl4. Control groups received either PRS, PRCs or olive oil for six days. Then, serum biochemistry (total protein, cholesterol, triglycerides and albumin) and oxidative stress parameters were measured.
ResultsWe showed that CCl4 treatment was associated with an increase of the serum aspartate amino transferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), cholesterol and triglycerides levels. In parallel, serum total protein, albumin and blood sugar levels were significantly decreased. Regarding the oxidative stress parameters, catalase and glutathione S-transferase (GST) levels were lower, conversely to the lipid peroxidation (MDA).
ConclusionOur results strongly support that administration of PRS and PRCs may significantly protect liver against CCl4-induced toxicity by enhancing antioxidative stress pathway and preventing lipid peroxidation.
Keywords: Carbon tetrachloride, Propolis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Oxidative stress, Hepatotoxicity -
Pages 198-204Background
Cynodon dactylon is a herbal medicine of interest in Iranian traditional medicine, which is used in cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and heart failure. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of total extract of C. dactylon rhizomes on myocardial infarction and on post myocardial infarction (MI) heart tissue injuries.
MethodsIsoproterenol (100 mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously for two consecutive days for induction of MI in rats and C. dactylon extract was administered orally twice daily started before isoproterenol injection for 4 consecutive days.
ResultsHistopathological analysis showed a marked increase in myocardial necrosis in rats with MI (p<0.001). Treatment with C. dactylon (200 mg/kg) significantly (P<0.05) decreased myocardial necrosis. Hemodynamic variables were significantly suppressed in MI group and treatment with C. dactylon improved the hemodynamic parameters (P<0.05). Our electrocardiogram analysis demonstrated that C. dactylon with all doses increased R-Amplitude and R-R Interval (p<0.05, p<0.01) which were suppressed in MI group. Furthermore in treated groups with 100 and 200 mg/kg, P-R interval was also significantly increased in compared to MI group.
ConclusionThis study demonstrated that C. dactylon can improve hemodynamic and electrocardiogram parameters in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction and thereby suggest that it can be used as a cardioprotective agent in myocardial infarction.
Keywords: Cynodon dactylon, Electrocardiogram, Hemodynamic, Isoproterenol, Myocardial infarction -
Pages 205-220Background
Pre-eclampsia (PE) contributes to the second cause of maternal death in Indonesia. Andaliman is a typical spice of the Batak ethnic in Northern Sumatera Province, Indonesia. This study aimed to explore the potential of novel herbal medicine compound of nanoherbal andaliman and extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) as PE treatment.
MethodsNanoherbal andaliman was generated using High-energy Milling (HEM). The treatments were divided into the following five groups: K- (control): pregnant rats; K+: PE model rats; P1: PE model rats + 0.45 g of EVOO/200 g BW on the 13th–19th day of pregnancy; P2: PE model rats + nanoherbal andaliman 100 mg/200 g BW on the 13th– 19th day of pregnancy; and P3: PE model rats + combination of 0.45 EVOO/200 g BW and nanoherbal andaliman 100 mg/200 g BW on the 13th–19th day of pregnancy. Rats were dissected on the 20th day of pregnancy. The observed parameters were blood pressure, proteinuria, malondialdehyde (MDA), Heat Shock Protein-70 HSP-70 and histology of placenta.
ResultsA significant difference was noticed (p<0.05) in blood pressure, proteinuria, foetal weight, haematocrit, erythrocytes and trophoblastic cells after the administration of combined nanoherbal andaliman and EVOO. No significant differences in placental weight, foetal number, leukocytes, MDA and HSP-70 were found (p>0.05).
ConclusionThe combination of nanoherbal andaliman and EVOO decreased systolic blood pressure and induced the expression of MDA and HSP-70, as well as placental histology of pre-eclamptic rats.
Keywords: Zanthoxylum acanthopodium, Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), Preeclampsia, HSP-70, MDA -
Pages 221-226Background
Frequent seizure is followed by overproduction of free radicals and brain oxidative stress. Renin angiotensin system (RAS) has some effects on central nervous system. We designed this research to challenge the effect of captopril as an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor against brain oxidative stress in pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) -induced seizures in mice.
MethodsThe groups were including (1) Control (saline); (2) PTZ (100 mg/kg, i.p.), (3-5) PTZ- captopril (Capto) that received three doses of Capto 10, 50 and 100 mg/kg 30 min before PTZ injection. Latency time in the onset minimal clonic seizures (MCS) and generalized tonic-clonic seizures (GTCS) were recorded. The level of malondialdehyde (MDA) and total thiol, as well as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activity in the hippocampus and cortex were measured.
ResultsAll doses of captopril postponed the onset of MCS and GTCS. Accumulation of MDA in the brain tissues of PTZ group was higher than control group, while total thiol content and CAT activity were lower. Pretreatment with captopril (100 mg/kg) diminished MDA concentration compared with PTZ group. Captopril (50 and 100 mg/kg) also increased the level of total thiol groups versus PTZ group. Captopril injection (50 and 100 mg/kg) elevated the activity of SOD and CAT in the brain tissues. In addition captopril administration diminished mortality rate caused by PTZ.
ConclusionFindings demonstrated that convulsions caused by PTZ were followed by oxidative stress status in the brain tissues. Pretreatment with captopril attenuated the effect of PTZ on brain tissue oxidative damage.
Keywords: Captopril, Pentylenetetrazole, Seizures, Mice, Oxidative Stress -
Pages 227-234Background
This study evaluated the possible protective effects of Gordonia bronchialis (Gb) on oxidative stress and some subsequent alterations on testis from rats undergoing an experimentally induced type 1 diabetes.
MethodsA total of 40 male rats were randomly divided into four groups of ten. Diabetes was induced by injection of 55 mg/kg streptozotocin in 30 rats. Oral administration of Gb at dose of 105 (low dose) and 107 (high dose) CFU/rat was performed in two groups continuously for 14 days. The third and fourth groups received normal saline as the diabetic and healthy control groups, respectively. The blood and testicular tissue samples were taken on the 14th and 21st days post treatment for biochemical and histopathological evaluations.
ResultsSignificant differences were found in blood glucose level, insulin, IL-6 and TNF-α values together with catalase and superoxide dismutase activities and malondialdehyde level in the diabetic group in comparison with healthy and Gb recipient groups. Moreover, the histopathological lesions observed in the diabetic rats mainly included basement membrane thickening, decreased number of Sertoli cells, and severe reduction of spermatogenesis markedly attenuated in Gb-treated rats.
ConclusionTaken together, it seems that oral administration of Gb could ameliorate testicular damage associated with some related parameters in the diabetic animal model.
Keywords: Biochemical evaluation, Histopathological lesions, Spermatogenesis, Reproductive system, oxidative stress -
Pages 235-243Background
The manuscript is aimed to optimize the biopharmaceutical parameters of a poorly soluble, neutral anti-rheumatic drug ‘leflunomide’ by preparing its non-covalent derivatives (NCDs). For this various monocarboxylic acids- (adipic acid, picolinic acid) and dicarboxylic acids (maleic acid, malonic acid, sorbic acid), as well as pyridine carboxamide derivatives (nicotinamide, isonicotinamide), are used as coformers.
MethodsThe novel solid forms were rationally prepared and systematically characterized. Further, these solid forms were subjected to equilibrium solubility and intrinsic dissolution rate (IDR) analysis in three aqueous media (pH 1.2, pH 4.5 and pH 6.8). In vivo plasma studies in male Wistar rats were done to assess the effect on area under the curve (AUC) and the maximum concentration (Cmax) of leflunomide in prepared solid forms.
ResultsThese NCD were primarily characterized to be eutectics rather than cocrystals as expected. The stoichiometry was established by phase diagrams. The negative value of heat of mixing indicated them to be of cluster type. In addition, leflunomide in eutectics showed approximately 9 folds increase in solubility up to 4 hours. Besides this, approximately 4 folds enhancement in the in IDR was also observed. Maximum increase in bioavailability indicated by enhanced values of AUC and Cmax (490.29 μg h-1 mL-1 and 31.42 μg mL-1, respectively) for leflunomide-maleic acid eutectic in comparison to pure LEF (AUC: 193.20 μg h-1 mL-1 and Cmax: 12.09 μg mL-1).
ConclusionThe unsuccessful cocrystallization experiments were found be the latent eutectics. The evaluation of these novel eutectics of poorly soluble drug exhibited possibility to further amplify the scope of accessible material phase options other than pure active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) without disturbing the structural integrity.
Keywords: Eutectics, Phase diagrams, Heat of mixing, Pharmaceutical properties, Physical stability -
Pages 244-253Background
To overcome low solubility of naproxen (NAP), deep eutectic solvents (DESs) based on choline chloride (ChCl) with glycerol (G) and oxalic acid (OA) as green solvents have been used up to 0.9 mole fraction of DES at T = (298.15 to 313.15) K.
MethodsDESs were prepared by combination of the two components with the molar ratios: ChCl/glycerol (1:2) and ChCl/oxalic acid (1:1). The solubility of NAP in the aqueous DESs solutions was measured at different temperatures with shake flask method.
ResultsThe solubility in these solvents increased with increasing the weight fraction of DESs, especially in ChCl/OA. The solubility data were correlated by e-NRTL, Wilson and UNIQUAC models. Also, the thermodynamic functions, Gibbs energy, enthalpy, and entropy of dissolution were obtained.
ConclusionOxalic acid based DES exhibits higher solubility than glycerol based DES. The thermodynamic models were successfully used to correlate solubility data. In addition, the results show that, the main contribution for NAP solubility in the aqueous DES solutions is the enthalpy.
Keywords: Deep eutectic solvents, Solubility, Naproxen, Activity coefficient models, Thermodynamic properties -
Pages 254-261Background
A new stability indicating RP-HPLC based assay method was developed to quantify ivermectin and praziquantel simultaneously and applied effectively to tablets.
MethodsThe simultaneous assay of ivermectin and praziquantel by RP-HPLC was done using an YMC C18 (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) column with a mobile phase mixture of 0.1M disodium hydrogen phosphate (pH 4.5) and acetonitrile (55:45, v/v) using a isocratic flow rate of 1.0 ml/min and measured at 242 nm using photodiode array detector. All parameters were validated following the ICH guiding principles. The method was applied to quantify ivermectin and praziquantel simultaneously in tablets.
ResultsThe retention values of ivermectin and praziquantel were 3.465 min and 4.468 min, respectively. The method’s linearity was found to be 1-3 µg/ml (ivermectin) and 25-75 µg/ml (praziquantel). The limit of detection was 0.010 µg/ml (ivermectin) and 0.046 µg/ml (praziquantel); limit of quantification was 0.033 µg/ml (ivermectin) and 0.155 µg/ml (praziquantel). The percent relative standard deviation of ivermectin and praziquantel was ˂1.0%. The percent assay was 99.51% and 99.20% for ivermectin and praziquantel, respectively. In tablets, the percent recovery of ivermectin and praziquantel was 99.60% and 99.38% with a percent relative standard deviation value of 0.353% and 0.106%, respectively. Stability indicating capability of the method was demonstrated through the stress degradation studies.
ConclusionThe developed method was proved to be selective, precise and accurate for the quality control of ivermectin and praziquantel in tablets.
Keywords: Ivermectin, Pranziquantel, Antihelmintic agent, Stress degradation, RP-HPLC, Analysis -
Pages 262-267Background
The present work is aimed to study the effect of different parameters on the fluorescence intensity of atenolol (ATE) and carvedilol (CAR) and optimization by response surface methodology (RSM) to provide a simple analytical method for their quantification in pharmaceutical formulations.
MethodsVarious parameters affecting the fluorescence intensity, i.e., sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) concentration, pH, volume fraction of solvents were optimized using RSM. Then, the optimized parameters were applied to the validation of a method for fluorimetric determination of β-blockers in their pharmaceutical preparations.
ResultsIt is obtained that under the optimum conditions for determination of ATE, the method provided a linear range between 130 to 750 ng/mL with a coefficient of correlation (r) of 0.9996. Also, the limit of detection and limit of quantification (LOD and LOQ) were 40 ng/mL and 130 ng/mL, respectively. Moreover, it is observed that, the linearity of method for determination of CAR was between 0.37 to 4.0 ng/mL and LOD and LOQ of method were 0.11 ng/mL and 0.37 ng/mL, respectively.
ConclusionAn accurate, sensitive and reliable spectrofluorimetric method was developed anf successfully used to determine the (ATE) and carvedilol (CAR) in their pharmaceutical preparations.
Keywords: Atenolol, Carvedilol, Spectrofluorimetry, Experimental design, Pharmaceutical preparations -
Pages 268-273Background
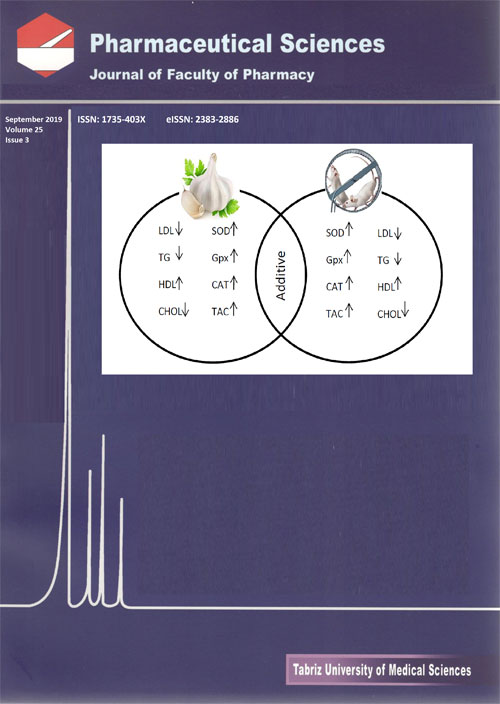
We evaluated the combination effect of voluntary exercise and garlic on serum oxidative stress biomarkers and lipid profile in healthy rats.
MethodsThe rats were randomly assigned to four groups (n=7): Control, Garlic, Exercise, and Garlic + Exercise. Rats were fed with raw fresh garlic homogenate by oral gavage (250 mg/kg) or were subjected to voluntary exercise using stainless steel running wheels alone or together for 6 weeks. The samples were collected at the end of the experiment.
ResultsAfter 6 weeks, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), triglycerides (TG) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels improved in both garlic and exercise group, compared with the control group. We also found that serum glutathione peroxidase (Gpx), Superoxide dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT), and Total antioxidant (TAC) levels enhanced significantly following the above-mentioned interventions. Furthermore, simultaneous treatment of rats with garlic and voluntary exercise had an additive effect on these parameters. However, malondialdehyde (MDA) level was not significantly different from control group during our protocol.
ConclusionThe findings revealed that simultaneous treatment of rats with garlic and voluntary exercise improved antioxidant defense system and lipid profile in an additive manner in healthy rats.
Keywords: Garlic, Voluntary exercise, Oxidative stress, Lipid profile -
Pages 274-277Background
Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet drug that is widely prescribed for cardiovascular disease. In cardiac surgery, it is used in patients after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) to prevent coagulation disorders. The irrational use of this drug can lead to bleeding and require surgical exploration along with increased therapeutic cost. Therefore, it is essential to study the pattern of clopidogrel use in hospitals.
MethodsThis study was conducted for a 6-month period to evaluate clopidogrel adherence to American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology (AHA / ACC) Guidelines in patients after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. Patients’ data were recorded in the pre-designed questionnaire, which included demographic data, past medical history, drug history along with the indications of clopidogrel use. Data analysis was performed by SPSS 16 software.
ResultsA total of 120 patients with a mean age of 61.3 ± 8.9 years old were recruited in to this study. Male to female ratio was 3 times. The main risk factors in patients with ischemic heart disease were male gender (74.2%), hypertension (80%), and smoking (47.5%). In addition to clopidogrel, most of the patients received aspirin (95.8%), followed by heparin (31.7%), and warfarin (5%) or enoxaparin (2.5%). The clopidogrel indications were non ST-elevation myocardial infarction / unstable angina (33.3%), acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (20.8%), recent myocardial infarction or stroke (3.3%), and CABG off-pump (30%). In 70.8% of cases, the administration of clopidogrel was consistent with AHA / ACC standard guidelines and most of the irrational cases belonged to the usage of the drug after on-pump CABG surgery.
ConclusionThe results showed that the rates of adherence to clopidogrel use with the AHA/ACC guidelines for patients who underwent CABG surgery was relatively good, but required further improvement.
Keywords: Clopidogrel, Aspirin, Coronary artery bypass grafting, Guideline


