فهرست مطالب
Pharmaceutical Sciences
Volume:27 Issue: 2, Jun 2021
- تاریخ انتشار: 1400/03/11
- تعداد عناوین: 16
-
-
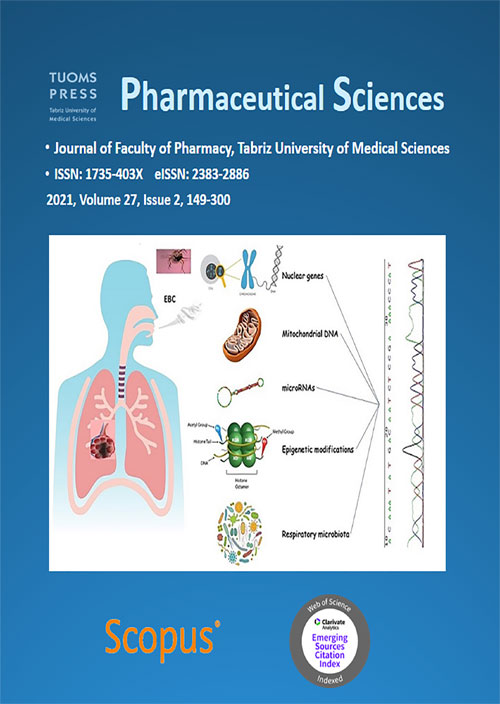
Pages 149-161
Lung diseases have been recognized as an extensive cause of morbidity and mortality in the worldwide. The high degree of clinical heterogeneity and nonspecific initial symptoms of lung diseases contribute to a delayed diagnosis. So, the molecular and genomic profiling play a pivotal role in promoting the pulmonary diseases. Exhaled breath condensate (EBC) as a novel and potential method for sampling the respiratory epithelial lining fluid is to assess the inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers, drugs and genetic alterations in the pathophysiologic processes of lung diseases. The recent studies on the analysis of EBC from both a genetic and epigenetic point of view were searched from database and reviewed. This review provides an overview of the current findings in the tracking of genomic and epigenetic alterations which are potentially effective in better management of cancer detection. In addition, respiratory microbiota DNA using EBC samples in association with pulmonary disease especially lung cancer were investigated. Various studies have concluded that EBC has a great potential for analysis of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA alterations as well as epigenetic modifications and identification of respiratory microbiome. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) based genomic profiling of EBC samples is recommended as a promising approach to establish personalized based prevention, diagnosis, treatment and post-treatment follow-ups for patients with lung diseases especially lung cancer.
Keywords: Exhaled breath condensate, Non-invasive, Lung, Genetic, Epigenetic, Personalized medicin -
Pages 162-169Background
Sepsis is a lethal clinical syndrome that results from dysregulated systemic inflammatory response of the body due to the invasion of pathogens, especially bacteria. Despite advances in medical care and therapy, sepsis is still one of the major causes of death in intensive care units and no decisive medical treatment is available against that. Studies have suggested that some Arum species have anti-bacterial properties. The present study investigated the effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Arum orientale, on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) induced sepsis in rats.
MethodsCLP method was used for induction of sepsis in rats. Hydroalcoholic extract of A. orientale was injected intraperitoneally with doses of 80 and 640 mg/Kg body weight at times of 0, 1, 3, 6 and 24 h after the surgery. Antibacterial activity, hemodynamic parameters, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and survival rate were measured after 72 h.
ResultsHydroalcoholic extract of A. orientale showed antibacterial activities as potent as gentamycin against Escherichia coli. Administration of the extract with a dose of 80 mg/Kg body weight increased significantly hemodynamic parameters such as mean arterial pressure (p<0.05)and decreased optical density (OD) (p<0.05) of blood. The extract also increased serum MPO activity (p<0.01) and reduced survival rate to 20%.
ConclusionThis study for the first time showed that hydroalcoholic extract of A. oriental acts as a double edge sword in the treatment of CLP-induced sepsis. This extract showed antibacterial properties and also improved hemodynamic parameters but decreased survival rate, that might be through pro-inflammatory effects.
Keywords: Arum, Anti-bacterial agent, Sepsis, Hemodynamics, Myeloperoxidase -
Pages 170-182Background
Ammoides pusilla plant is a species of therapeutic interest which used in traditional medicines. This work aims to valorize this plant by the characterization of their bioactive components and the evaluation of the in vivo anti-inflammatory potential against a severe disease affecting the bone structure and the stability of the articular cartilage.
MethodsFirst, the phytochemical screening of the polyphenolic extracts of A. pusilla was carried out. The second part of our study is devoted to the evaluation of the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of the aqueous extract of A. pusilla based on the method of Freund's adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis.
ResultsPhytochemical tests demonstrated the richness of extract with flavonoids, tannins, coumarins, anthocyanins and triterpenes. Whereas, the quantitative determination reveals that the aqueous extract of A. pusilla is the richest with bioactive components with contents of total polyphenols, flavonoids and tannins equal to 9.52 ± 0.11 mg gallic acid/g, 4.75 ± 0.05 mg quercetin/g and 8.64 ± 0.02 mg catechin/g respectively. The results of the anti-inflammatory activity showed that the aqueous infused extract of A. pusilla has an interesting antiarthritic potential on Freund's adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis in mice. It is manifested by a weight gain; a normal arthritic index and biochemical parameters close to those of Diclofenac®.
ConclusionThe aqueous infused extract of A. pusilla is therefore of considerable therapeutic interest as an alternative compound for the prevention of inflammation and for the improvement in bone structure.
Keywords: Ammoides pusilla, Rheumatoid arthritis, Anti-inflammatory, Polyphenols, Toxicity -
Pages 183-193Background
Food additives are widely used in energy drinks and when taken above acceptable daily intake leads to various neurodevelopmental toxic effects. The present study aimed to evaluate the neurodevelopmental toxic effects in rat pups after pre and postnatal administration of selected food additives in pregnant animals.
MethodsPregnant rats aged 160-180 days were divided into six groups with four animals per group. Group 1 treated with vehicle, group 2 standard (caffeine 25 mg/kg p.o.), groups 3-6 were treated with glucuronolactone (5 mg/kg p.o.), taurine (8 mg/kg p.o.), gluconolactone (84 mg/kg p.o.), and combination of food additives respectively till postnatal day (PND) 15. After PND 21, pups were evaluated for neurobehavioural parameters using the behavioral alteration test, Morris water maze test, locomotor activity test, Y-maze test, hot plate latency and neurobehavioural scoring. Neurotransmitters were estimated in brain tissue extract on PND 30, 45 and 60 and histological observations were examined in the brain cortex region.
ResultsFood additive treated groups showed an increase in behavioral activity, escape latency, immobility, percentage of alterations, hot plate latency and neurobehavioural scoring at selected dose and combination compared to control (p<0.001). The decrease in neurotransmitter levels in the brain and marked degeneration of neurons in the cortex were observed significantly in group6 pups.
ConclusionThe present results corroborate that food additives in combination induced neurodevelopmental toxic effects further mechanistic studies are suggested to understand the synergistic effect.
Keywords: Energy drinks, Food additives, Glucuronolactone, Neurodevelopmental toxic effects, Cytotoxicity -
Pages 194-200Background
Chemotherapy drugs such as vinblastine cause oxidative stress in the bone marrow resulting changes in blood cell production and anemia. In this study, the antioxidant and therapeutic potential of quercetin was evaluated.
MethodsTwenty-one male Wistar rats were divided into three groups; The Control group received a daily dose of normal saline, group 2 received a single dose of 2 mg/kg b.w. vinblastine intraperitoneally (i.p.) on the first day of study, and group 3 received a single dose of vinblastine (2mg/kg b.w. i.p.) along with quercetin (20 mg/kg b.w. i.p.) for 14 days. To evaluate oxidative stress in bone marrow; malondialdehyde (MDA), Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) and Pro-Oxidant/Antioxidant Balance (PAB) were also measured using specified methods.
ResultsThe blood analysis showed that the mean level of RBC, Hemoglobin, and Hematocritwere significantly higher in the vinblastine group compared to the control group. Treatment with quercetin could elevate them into the normal range. Administration of vinblastine elevated the levels of bone marrow MDA and PAB significantly (p<0.05) compared to the control group but had no effect on total antioxidant capacity. The use of quercetin with vinblastine showed a decrease in the levels of bone marrow MDA and PAB compared to the vinblastine group alone.
ConclusionThe findings of this study showed that quercetin at a dose of 20 mg/kg could improve the anemia induced by vinblastine chemotherapy, and it can also be useful in improving vinblastine-induced lipotoxicity.
Keywords: Vinblastine, Quercetin, Oxidative Stress, Anemia -
Pages 201-208Background
The recent studies emphasized on the correlation of vancomycin antibacterial effect with pharmacokinetics properties such as the area under the curve/minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC24/MIC) ≥400 and serum trough level 15-20 mg /L in the patients with severe infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The purpose is to assay the vancomycin pharmacokinetic properties in our population and evaluates the correlation between AUC24/MIC and trough serum level of vancomycin in given patients.
MethodsThe patients with a positive MRSA culture, treated with vancomycin, were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. Three plasma samples were obtained during the study including 30 min before fourth and the fifth dose as trough levels and 1 hour after the fourth dose as peak level to determine AUC24. E-TEST determined the MIC of vancomycin.
ResultsThirty-eight patients with an average age of 48.33±16.44 were enrolled in this study. The mean ± SD of MIC was 0.99±0.30 mg/L. Thirty-four patients reached the adequate therapeutic range of AUC24/MIC ≥ 400 due to the standard vancomycin dosing method. In comparison, only 7 and 10 patients had the first and second trough levels in target intervals of 15-20 mg/L, respectively. Due to the receiver operating characteristic curve test (ROC test), the trough level after the fourth dose had a strong correlation with target AUC24/MIC with a sensitivity of 94.1%and specificity of 75.0%.
ConclusionThis study concluded using only a trough level is not appropriate for therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of vancomycin. In our population, target AUC24/MIC (≥ 400) had a reasonably strong correlation with the trough level before the fifth dose which achieved with trough level ≥10.81 mg/L and MIC< 1 mg/L.
Keywords: -Vancomycin, AUC24, MIC, Trough serum level, Methicillin-resistant, Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Therapeutic drug monitoring(TDM) -
Pages 209-218Background
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) are responsible for several pathological conditions such as the development of different kinds of tumors. The combined inhibition of both signal transduction pathways seems to be a promising novel approach for cancer treatment.
MethodsIn this study, novel 4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives with various substituents on-7 position of quinazoline moiety were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for their antiproliferative activity against A431 and HU02 cell lines.
ResultsCompounds 8a, 8d, and 8f displayed the most potent anticancer activities against A431(IC50 = 1.78 μM, 8.25 μM, and 7.18 μM, respectively) in comparison with reference standards(erlotinib IC50=8.31 μM and vandetanib IC50=10.62 μM). Molecular docking studies proved that8a as the most potent compound could be efficiently accommodated in the ATP binding site ofEGFR and VEGFR-2 through the formation of essential hydrogen bonds between quinazolineN1 atom and the Met796 backbone of EGFR as well as the Cys919 backbone of VEGFR-2 with a distance of 1.94 Å and 1.398 Å, respectively.
ConclusionCompound 8a as the most potent compound with morpholine and 3-bromoaniline at the 7 and 4 positions of quinazoline scaffold, respectively, deserves more study and structural optimization as an anticancer agent.
Keywords: Synthesis, Antiproliferative activity, 4-anilinoquinazoline, Molecular modeling -
Pages 219-229Background
Retapamulin is the first pleuromutilin antibacterial approved for the treatment of impetigo. The objective of the current research was to utilize the design of experiments approach for development and optimization of robust RP-HPLC method for the quantitation of Retapamulin in marketed cream and in-house developed microemulsion based formulations with an oily matrix.
MethodsThe impact of various chromatographic conditions (independent variables) was assessed using Plackett–Burman design on critical analytical attributes (response) to screen initial experimental conditions. The Box-Behnken design was employed to optimize the selected chromatographic factors on the responses. Further, validation of optimized RP-HPLC was carried out as per the ICHQ2(R1) guideline.
ResultsPareto ranking analysis showed that % organic phase, flow rate, and volume of injection were found statistically significant (p < 0.05) variables influencing the retention time, number of plates, and tailing of the Retapamulin peak. The optimized RP-HPLC method with the stationary phase, C18 (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) column, and mobile phase as a mixture of methanol and potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0, 90:10 % v/v, isocratic), the flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, 10 μL injection volume, 25°C column oven temperature, 247 nm as detection wavelength, was successfully validated based on ICHQ2(R1) guideline.
ConclusionRP-HPLC method was successfully used to separate (retention time 4.34 ± 0.2 min)and assay Retapamulin in microemulsion and marketed cream. The outcomes of the investigation exhibited the effective application of a multivariant approach in the optimization of the RP-HPLCfor routine analysis of Retapamulin.
Keywords: Box, Behnken design, Cream, Microemulsion, Plackett, Burman design, Retapamulin -
Pages 230-237Background
Nanoemulsions are colloidal transparent systems for the delivery of hydrophobic drugs. This study aimed to determine the effect of parameters affecting particle size of a nanoemulsion containing ibuprofen using artificial neural networks (ANNs).
MethodsNanoemulsion samples with different values of independent variables, namely, concentration of ethanol, ibuprofen and Tween 80 as well as exposure (homogenization) time were prepared and their particle size was measured using dynamic light scattering (DLS). The data were then modelled by ANNs.
ResultsFrom the results, increasing the exposure time had a positive effect on reducing droplet size. The effect of concentration of ethanol and Tween 80 on droplet size depended on the amount of ibuprofen. Our results demonstrate that ibuprofen concentration also had a reverse relation with the size of the nanoemulsions.
ConclusionIt was concluded that to obtain minimum particle size, exposure (homogenization)time should be maximized.
Keywords: Artificial neural networks, Ibuprofen, Nanoemulsion, Particle size -
Pages 238-250Background
Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using medicinal plant extract is an emerging area of research due to their applicability in nanomedicines.
MethodsIn this study, aqueous extracts prepared from fruit-pericarps of two Garcinia species, G. indica (GI) and G. cambogia (GC) fruits which are important medicinally and commercially have been utilized for the synthesis of AuNPs. Various analytical techniques were utilized to characterize the synthesized AuNPs. The synthesized AuNPs were investigated for their biological properties such as antioxidant activity using the (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) DPPH model, cytotoxicity against MCF-7 (breast) cancer cell line, and antibacterial activity against two bacterial strains viz. B. subtilis and E. coli.
ResultsThe absorption peak of the AuNPs is observed at 541 nm using UV–Visible spectroscopy. The high resolution – scanning electron microscopy images showed spherical with a triangular shape AuNPs and their average sizes were ranging from 2 – 10 nm and it was found to be in good agreement with the particle size of 8 – 11 nm determined using X-ray diffraction analysis. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy revealed that water-soluble biomolecules from the aqueous extracts of the Garcinia species played a crucial role in the formation of AuNPs. The synthesized AuNPs exhibited considerable cytotoxicity with IC50 values 34.55 µg/ml (GI) and 35.69 µg/ml (GC) against the MCF-7 cancer cell line. Furthermore, synthesized AuNPs also demonstrated significant antioxidant and antibacterial properties comparable to the standards used.
ConclusionAuNPs have been synthesized using a simple green approach. The synthesized AuNPs demonstrated promising cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties.
Keywords: Garcinia, Extract, AuNPs, Antioxidant, Cytotoxicity -
Pages 251-261Background
Nowadays despite conventional methods in colon cancer treatment, targeting vital molecular pathways and induction of various forms of cell death by safe probiotic components like exopolysaccharides (EPSs) are of great importance and are considered as potential therapeutic agents. This study aimed to investigate the inhibitory effect of the EPS of L. paracasei on different colon cancer cell lines (SW-480, HT-29, and HCT-116).
MethodsFor this purpose, several cellular and molecular experiments including MTS assay, DAPI staining, Annexin V/PI assay, quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and some important ferroptosis-related assays were performed.
ResultsBased on the findings, L. paracasei EPS can induce apoptosis confirmed by all apoptosis related assays and could not act through ferroptosis pathways. L. paracasei EPS could hinder the Akt1, mTOR, and Jak-1 mRNAs, and induces apoptosis through down-regulation of the antiapoptotic gene (Bcl-2), up-regulation of pro-apoptotic genes (BAX, caspase-3, 8).
ConclusionThe exploited EPS of an indigenous probiotic strain with anticancer potential with low/insignificant cytotoxicity to normal cells is proposed for future applications in molecular targeted therapy of colon cancer treatment. Furthermore, in vivo and clinical trials should be performed to evaluate the applicability of this component besides conventional methods to increase the survival rate of colon cancer patients.
Keywords: Apoptosis, Colon cancer, Exopolysaccharides, Ferroptosis, Probiotics, Signaling pathways -
Pages 262-267Background
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Probiotics are useful and non-pathogenic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract, which can show anticancer activity through the induction of apoptosis. This study aimed to evaluate the antiproliferative effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus probiotic on the Caco-2 colorectal cancer cell line.
MethodsThe supernatant (secreted metabolites) and bacterial extract of L. acidophilus probiotics were prepared and used as an anti-proliferative agent on the colorectal cancer cell line, Caco-2 in vitro. The effects of supernatant and extract of L. acidophilus were evaluated on the viability and proliferation of cancer cells using MTT assay. Moreover, morphological alterations of cancer cells treated with supernatant and extract of L. acidophilus were evaluated by an inverted phase contrast microscope. The mRNA expression levels of apoptosis-related genes (SURVIVIN and SMAC) in treated cancer cells and untreated controls were evaluated using the Real-Time PCR method.
ResultsThe results showed that the supernatant and extract of L. acidophilus inhibited the viability and proliferation of cancer cells in a dose and time-dependent manner. Moreover, various morphological alterations were observed in the treated cancer cells, which are indicators of apoptosis induction. The mRNA expression of SURVIVIN and SMAC genes were significantly up-regulated and downregulated in the treated cancer cells, respectively.
ConclusionThe results of the present study suggested that the supernatant and extract of L.acidophilus could inhibit the viability and proliferation of colorectal cancer cell line, Caco-2through induction of apoptosis, increase the survival rate of colon cancer patients.
Keywords: Apoptosis, Colorectal cancer, Lactobacillus, Probiotics -
Muscodor sp. IBRL OS-94, A Promising Endophytic Fungus of Ocimum sanctum with Antimicrobial ActivityPages 268-280Background
An endophytic fungus, Muscodor sp. IBRL OS-94 isolated from the leaf of Ocimum sanctum was believed to possess significant antimicrobial activity and several assays were carried out to evaluate its pharmaceutical potential.
MethodsAgar plug diffusion and the disk diffusion assays were performed to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of the fungal extract. Also, the broth microdilution assay was done to investigate the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the fungal extract. Meanwhile, the scanning electron microscope (SEM) was employed to observe the structural degeneration of the microbial cells treated to the extract.
ResultsThe results revealed that fungal isolate showed favorable antimicrobial activity through agar plug diffusion assay and the disk diffusion assay demonstrated that most of the test microorganisms were susceptible to extracellular extract compared to extracellular extract. As for the MIC and MLC values, the extracellular fungal extract exerted a bactericidal/fungicidal effect against all five Gram-positive bacteria, four Gram-negative bacteria, one yeast, and none of the test fungi. Meanwhile, the intracellular fungal extract exhibited bactericidal/fungicidal activity against three Gram-positive bacteria, one Gram-negative bacterium, and one yeast. The structural degeneration study via SEM revealed that various cell abnormalities including severe damage to the cell wall which led to microbial cell death.
ConclusionThe present study suggests the fungal extract from Muscodor sp. IBRLOS-94 as an antimicrobial agent.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity, Muscodor sp. IBRL OS-94, Agar plug diffusion assay, Disk diffusion assay, MIC, MLC values, Structural degeneration -
Pages 281-290Background
Oxidative stress caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation has been associated with dermal problems, including skin cancer. In this study, we determined the photoprotective and antioxidant activity of isolated metabolites from the lichen Bunodophoron melanocarpum (Sphaerophoraceae) to find new sunscreens prototypes.
MethodsThe constituents of B. melanocarpum were isolated by phytochemical methods and their structures were determined by spectroscopy (IR, 1D and 2D NMR). Antioxidant activity was measured by scavenging DPPH free radicals (EC50), ferric reducing power (FRP), and inhibition of lipid peroxidation (% ILP). The photoprotective capacity against ultraviolet(UVA and UVB) radiations was determined in vitro by calculating their sun protection factor(SPF), critical wavelength and UVA ratio and these values were compared against commercial sunscreens. The lipophilicity and possible skin penetration to the lipid-rich stratum corneum of the isolates, was determined by calculating their octanol/water partition coefficients (Log P) and Gibbs free energy of transfer (ΔtG0 ).
ResultsSphaerophorin (1), everninic acid (2), sphaerophorol carboxylic acid (3) and friedelin(4) were isolated from B. melanocarpum. Orsellinic acid-type compounds 1 and 3 are dual agents with antioxidant capacity as free radical scavengers (EC50= 0.0857 and 0.1828 mol compound /mol DPPH•, respectively) and photoprotective properties particularly against UVB radiation(SPF 25.78 ± 0.53 and 22.00 ± 1.03, respectively). In addition, they had lipophilicity (Log P 7.07 ±0.64 and 4.03 ± 0.32, respectively) and ΔtG0 (-40.32 ± 3.67 and -22.97 ± 1.82 kJmol-1, respectively)suitable to act on the skin.
ConclusionSphaerophorin (1) and sphaerophorol carboxylic acid (3) are dual agents with antioxidant and UVB photoprotective properties and are also lipophilic substances that spontaneously would diffuse across the skin.
Keywords: Skin cancer, Photoprotectors, Free radical scavengers, Photoaging -
Pages 291-295Background
Traditionally, Usnea genus has significant uses in the treatment of swelling and tumors in Africa and Asia. The aim of the present study was to investigate the chemical constituents present in the acetone extract (AE) of Usnea subfloridana Stirton and also to evaluate their anti-inflammatory and anti-gout effects.
MethodsIsolation and characterization of secondary metabolites from AE were evaluated by chromatography and spectral studies. Anti-inflammatory activities were assessed through cyclooxygenase (COX1 and COX2) and 5-lipooxygenase (5-LOX) enzyme inhibition assays, while anti-gout effects were evaluated by xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibition assay.
ResultsThe existence of five known depsidones, identified as galbinic acid (1), conprotocetraricacid (2), constictic acid (3), salazinic acid (4), and lobaric acid (5), were exposed by chemical investigation of AE and confirmed by spectral data. Using in vitro enzyme inhibition assays, it was noticed that all the isolates showed dose-dependent activity against all the tested enzymes. Mainly, compounds 2 and 5 showed better inhibition efficiency on COX2 enzyme with the IC50of 7.17±1.07 and 7.01±0.94 nM, respectively, than the reference drug indomethacin (7.3±0.65nM). Furthermore, all isolates exhibited potent inhibition effects on the XO enzyme.
ConclusionThe results indicated that U. subfloridana can be a favorable natural source for thetreatment of inflammation and gout. Compounds 2 and 5 were responsible for these biologicalactions by regulating pro-inflammatory enzymes, namely COXs, 5-LOX, and XO.
Keywords: 5-Lipoxygenase, Anti-inflammation, Cyclooxygenase, Enzyme inhibition, Usnea subfloridana, Xanthine oxidase -
Pages 296-300Background
Ethanol is considered as a toxic compound when used in excess amounts. The toxic concentration for ethanol was reported to be 1000 – 2000 μg.mL-1 in plasma and serum samples. The aim of the current study was to develop a rapid and catalyst free colorimetric method for determination of ethanol in exhaled breath condensate (EBC) sample.
MethodsA redox reaction with dichromate-based colorimetric method was used for determination of ethanol in EBC.
ResultsThe proposed method shows a good sensitivity and selectivity for ethanol in compared with other compounds and biomarkers existing in EBC. The color change can be easily observed by the naked eye in the presence of ethanol in the range of 300 - 8000 μg.mL-1. The quantitative detection of ethanol was fully validated and used for determination of ethanol in EBC of alcohol administrated individuals.
ConclusionThis catalyst free colorimetric method has great potential for ethanol determination owing to many desirable properties such as high reliability, high sensitivity, and fast response time.
Keywords: Ethanol, Exhaled breath condensate, Redox reaction, Colorimetry


