فهرست مطالب
Pharmaceutical Sciences
Volume:28 Issue: 2, Apr 2022
- تاریخ انتشار: 1401/02/26
- تعداد عناوین: 16
-
-
Pages 174-193
In the pharmaceutical industry, liposomes and polymeric nanoparticles are the two most commonly studied delivery vehicles. A new technique uses lipid-polymeric hybrid nanoparticles (LPHNPs) with a polymeric core, and a shell made up of lipid-lipid-PEG lipids. They have properties which complement polymer nanoparticles and liposomes, and they have the potential to improve the physical stability and biocompatibility of the active pharmaceutical ingredient encapsulated in them. Evaporating the solvent from a dual-phase solution containing lipid and polymer is one of the most effective methods for producing lipid polymeric hybrid nanoparticles. The LPHNPs applications have also been significantly expanded to include combinational and active targeted drug delivery, as well as delivery of genetic materials, vaccines, and diagnostic imaging agents, in addition to single drug delivery for anticancer therapy, like Glioblastoma. The main agenda of this compilation was to address the effects of LPHNPs on Glioblastoma treatment. This compilation also highlights some of the formulation techniques and issues that arise during the preparation of LPHNPs. This review also discusses recent developments in core-shell lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles, which were conferred in considerable detail later in this article. The main issue which arises while using nanoparticles with polymer is entrapment efficiency. Because of their hybrid components, LPHNPs have proven to solve this problem to a large extent. The recent research trends suggest that lipid polymeric hybrid nanoparticles will prove to be highly effective or productive in treating diseases such as Glioblastoma.
Keywords: Lipid Polymer hybrid nanoparticles, Lipid-based nanoparticles, Glioblastoma, TPGS, Core shell-type lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles, Drug delivery -
Pages 194-207
Vitamin D (VD) deficiency is a significant issue affecting a large population around the world. As its natural sources are limited, people must constantly fortify their VD. Encapsulating VD increases its bioavailability and stability during processing and storage; hence it has promising potential to avoid VD deficiency. This study reviews current methods of VD fortification and encapsulation. Two predominant methods of VD fortification, i.e., biofortification and direct fortification, are advantageous over VD supplementation. However, significant VD losses occur during processing, storage, and passing across the stomach which can be minimized through encapsulation methods, i.e., micro and nanoencapsulation. Moreover, the capsule features like size, wall-to-core ratio, wall material, carrier oil composition, and encapsulation technique significantly affect VD bioavailability. To assess the optimum encapsulation procedures and possible risks in food fortification, comprehensive in vitro and in vivo studies must be conducted. Depending on the staple food products of a specific region, both VD fortification strategies have great potential in different countries. Besides, the risk of VD overdose due to fortifying a single staple food product is higher than fortifying various staple food products.
Keywords: Encapsulation, Vitamin D, Fortification, Bioavailability, Enrichment, Food -
Pages 208-223
Cancer is still a serious disease with high incidence over the past decades. Many anticancer drugs are discovered and used to treat cancer, among them, taxanes such as paclitaxel and docetaxel have high lipophilicity and low aqueous solubility which is further magnified considering the strong need for administering them by intravenous infusion. Currently, the poor water-solubility of taxanes is improved by prodrug formation, conjugation, inclusion complexation, micellar solubilization and liposome-based formulations. Recent achievements for solubilization of taxanes are reviewed and critically discussed regarding their pharmaceutical and chemical applications.
Keywords: Paclitaxel, Docetaxel, Taxanes, Poor water-solubility, Solubilization methods -
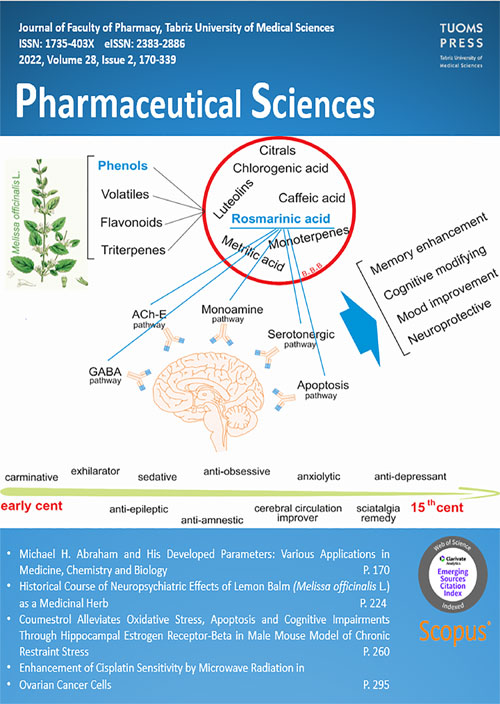
Pages 224-231
Affective disorders have become prevalent and costly worldwide chronic conditions. Lemon Balm (Melissa officinalis L.) is a medicinal plant with beneficial effects on neuropsychiatric disorders. Its potential to specifically treat conditions such as depression and anxiety has been investigated for over 20 centuries. Given the lack of a historical overview of lemon balm in mood disorders, the present review aimed to introduce the historical course of the neuro-psychiatric applications of lemon balm across the centuries. We investigated several viable medieval Arabic sources up to the 15th century, to distinguish the neuropsychiatric applications, especially anxiolytic and anti-depressive effects of lemon balm. In the early centuries, lemon balm was mainly prescribed to treat gastrointestinal disorders. Over time, physicians identified the efficient use of lemon balm in sadness, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression, epilepsy, ischemic stroke, amnesia, sciatalgia, and radicular neuropathy. Importantly, it was established that the therapeutic effects of lemon balm in the field of neuro-psychiatric diseases were emphasized by physicians during the Middle Ages. These findings have since been validated in human clinical trials. Lemon balm has also demonstrated the ability to be utilized in epilepsy, amnesia and ischemic stroke. Based on the extensive history of lemon balm in neuropsychiatry, future investigations could use this knowledge to extensively investigate the potential of lemon balm in neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety, and possibly develop an efficient neuropsychiatric remedy.
Keywords: Melissa officinalis, Lemon Balm, Neuropsychiatric disorders, Herbal medicine -
Pages 232-238Background
Rosa damascena Herrm (R. damascena) is a species of the Rosaceae family. The R. damascena has been shown to improve depression, anxiety and grief. It also suppresses allergic reactions and migraine headache. In addition, amelioration of learning and memory deficits, delay in onset of seizure attacks, alleviation of pain and improvement of sleep disorders have been attributed to extract and essential oil of R. damascena. This review was conducted to integrate the neuropharmacological effects of R. damascena.
MethodsEmployed scientific databases for collecting information were including PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar.
ResultsThe results of animal and clinical trial studies indicate that the extract of R. damascena and its essential oil apply useful therapeutic effects on depressant and anxiety-like behaviors, epileptic seizures, learning and memory impairments, sleep disturbances and pain.
ConclusionBased on scientific findings, the neuroprotective effects of R. damascena can be mainly linked to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Keywords: Rosa damascena Herrm, Nervous system, Neuropharmacological -
Pages 239-250Background
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a psychiatric condition that manifests through a broad range of symptoms and shares several phenotypes with anxiety and depression. Refractory PTSD affects 10–30% of the patients and highlights the need for alternative pharmacotherapy. The suggested involvement of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) with the emotional processes has enlightened the use of Cannabis sp. Then, this study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effects of a broad-spectrum Cannabis oil on anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors triggered by stressors from combined nature. In addition, this study investigated the effect of the oil on central cannabinoid receptor 1 and serum levels of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors.
MethodsMice were randomized into five groups (vehicle; Cannabis oil; fluoxetine; single oral dose) and submitted to acute restraint and chronic unpredictable stress. Then, they were behaviorally assessed in the elevated plus-maze test (EPMT), forced swimming test (FST), splash test (ST), and open field test (OFT). The tetrad cannabinoid assay evaluated the central effect of the oil. Serum biomarkers levels were measured by a multiplex bead-based assay.
ResultsCannabis oil (0.1 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly reduced the anxiety-like behavior in EPMT in the acute restraint stress model (p < 0.05) as compared to vehicle. Moreover, compared to the vehicle, Cannabis oil significantly reverted the despair and anhedonic-like behaviors in FST (p < 0.05) and ST (p < 0.05), respectively, in chronically stressed mice. Yet, compared to vehicle, therapy with Cannabis oil did not induce cannabinoid-tetrad (p < 0.0001); downregulated granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF; p < 0.01) and advanced glycation end-products (RAGE; p < 0.0001); and upregulated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF; p < 0.01) serum levels.
ConclusionAltogether, our data suggest the potential of the broad-spectrum Cannabis oil to improve symptoms related to anxiety and depression caused by traumatic events.
Keywords: Anxiety, Broad-spectrum Cannabis oil, Cannabis sp, Depression, Posttraumatic stress disorder -
Pages 251-259Background
Methamphetamine (METH) is considered the second most commonly abused drug in the world. There is limited or no evidence concerning the effective treatment of METH withdrawal symptoms, such as depression and anxiety. Mode of action of selegiline (increase of the brain neurotransmitter activity) suggests that it might be useful in METH withdrawal syndrome treatment, being capable of diminishing the preference and depression involved in drug degeneration and addictive activities.
MethodsMice were randomly divided into 10 groups (n= 10): five METH-nondependent groups treated with normal saline intraperitoneal (i.p) for two weeks, to which, from the 15th day, selegiline (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg; i.p) or fluoxetine (5 mg/kg; i.p) was administrated for 10 consecutive days. Other groups injected METH (2 mg/kg, at 12-h intervals) for 14 days. From the 15th day, the 10-day period of METH abstinence started and the above-mentioned doses of selegiline or fluoxetine were injected. Then, the mice were evaluated for depression and biochemical assessments from the 25th day of the study.
ResultsThe data indicated that post-treatment with selegiline (10-40 mg/kg; i.p) for 10 days reversed METH-induced depressive-like behaviors in the forced swimming test (FST), tail suspension test (TST), and splash test with exerting no effects on the locomotor activity. Furthermore, none of the previously proposed treatments affected the behavioral abnormality in the control animals. Moreover, both selegiline and fluoxetine as standard antidepressant drug, substantially improved the levels of mitochondrial reduced glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
ConclusionOur findings demonstrated that selegiline produced antidepressant-like effects following METH withdrawal and prevented the mitochondrial dysfunction in the male mice.
Keywords: Selegiline, Methamphetamine, Depression, Mitochondrion, Oxidative stress, Fluoxetine -
Pages 260-274Background
Coumestrol is well-known as a natural estrogen receptor-beta modulator. Since the role of estrogen receptors in controlling stressful situations has already been reported and their cognitive functions in hippocampus seem to be independent of sexual tasks, the aim of this study was to investigate the improving effects of this phytoestrogen on negative consequences of exposing male mice to chronic restraint stress.
MethodsThis study was divided into two separate but consecutive phases. In the first phase, the possible effects of coumestrol (30, 60, 120 µg.kg-1.day-1, i.p.) and its vehicle (sesame oil) on restraint stress-induced cognitive impairments, oxidative stress and apoptosis were evaluated. During the second phase, a selective estrogen receptor-beta antagonist was used to investigate the possible involvement of beta-type estrogen receptors in these processes. Morris water maze and novel object recognition tests were performed to evaluate memory while elevated plus maze and open field tests were used to measure the level of anxiety. Spectroscopy and western blotting methods were also employed to evaluate oxidative and apoptotic status in hippocampal tissues. Furthermore, serum level of corticosterone was measured for each group.
ResultsBehavioral tests indicated memory enhancing and anxiolytic effects of coumestrol. Biochemical evaluations also proved its antioxidant and anti-apoptotic potential. On the other hand, the mentioned behavioral and biochemical improvements were reversed in the group treated with estrogen receptor-beta antagonist.
ConclusionCoumestrol may ameliorate negative consequences of exposure to chronic stress such as oxidative stress, apoptosis and cognitive impairments, via the modulation of beta-type estrogen receptors in hippocampus.
Keywords: Coumestrol, Estrogen receptor-beta, Chronic restraint stress, Cognitive impairments, Apoptosis, Oxidative stress -
Pages 275-284Background
According to the Iranian Traditional Medicine (ITM) references, Platanus orientalis L. possesses wound healing properties. Herein, we developed different topical formulations based on the ethanolic extract of P. orientalis leaves and evaluated its wound healing effects through an in vivo model.
MethodsHydroalcoholic extract of the leaves was obtained from ethanol 80% and it was evaluated for DPPH radical scavenging activity, total phenolic and flavonoid contents as well as the presence of tannins. Different topical formulations including ointment (D-O) and polymer film (D-F), were prepared and an in vivo test was run for 14 days in an excision wound model consisting of 5 groups of 6 rats.
ResultsThe results indicated the higher efficacy of D-O compared with D-F, as wound surface area remarkably reduced within 14 days post-injury. Also, histological features including epitheliogenesis score, neovascularization, and collagen density indicated the potential wound healing effect of D-O.
ConclusionWound healing properties of the ethanolic extract of P. orientalis leaves depended on the type of formulation and D-O was found to be much more potent than D-F, from reducing wound surface area, maximum epitheliogenesis score, proper neovascularization pattern, and early type I collagenization points of view.
Keywords: Platanus orientalis L., Wounds, Topical formulations, in vivo, Histopathology -
Pages 285-294Background
Oral contraceptives are very widely used agents to check unwanted pregnancies.They contain synthetic analogues of estrogen and progesterone hormones. Estrogen is an important hormone that plays a significant role in menstrual cycle, ovulation, fertilization and implantation. Estrogen receptor α (ERα) can modulate the ovulation, fertilization or receptivity of the uterus. Oral contraceptives pose mild to severe adverse effects such as menstrual cycle disorders, metabolic alterations and increased risk of cancers. It is essential to identify and screen alternative contraceptives that are safer to use. The present study was aimed at identifying the compounds from Cissampelos pareira that is traditionally used for antifertility activity.
MethodsThe compounds reported from the plant were collected and prepared using the LigPrep wizard. The protein, ERα was selected from protein data bank (1G5O) and prepared. The ligands were docked with the protein and the hits were selected for further screening of free energy calculation, induced fit docking and molecular dynamics simulations based on the respective scores and various interactions.
ResultsAmong various compounds, Coclaurine and Norruffscine have been identified to interact with ERα and possess similar interactions as that of the endogenous ligand, estradiol. The compounds also showed drug-like properties in Qikprop analysis and promising result in the molecular dynamics simulation studies.
ConclusionConsidering the dock scores, molecular interactions with the ERα receptor and energy calculations, the compounds Coclaurine and Norruffscine were found to have good binding properties. Further in vitro and in vivo evaluations are warranted for confirmation.
Keywords: Antifertility, Cissampelos pareira, Estrogen receptor α, Virtual Screening, Molecular Dynamics -
Pages 295-303Background
Nowadays, ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer worldwide. Tumor debulking surgery followed by Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is the first line of ovarian cancer therapy. However, many patients experience a relapse of the disease due to chemotherapy resistance. Accordingly, this study aims to investigate the ability of microwave (MW) radiation to increase the susceptibility of ovarian cancer cells toward Cisplatin (Cis).
MethodsFirstly we designed a hand-made electromagnetic field exposure system and CO2 incubator to irradiate cells with a frequency equal to 2450±30 MHz and a power density of 2.47 mW/cm2 at a distance of 30 cm from the antenna. Two ovarian cancer cell lines A2780 (Cisplatin-sensitive) and A2780CP (Cisplatin-resistant) were subjected to either Cis, MW alone or Cisplatin + microwave radiation (Cis+MW). Cell viability, apoptosis, and P53 gene expression were assessed following drug/radiation exposure.
ResultsAfter 48 hours of treatment the combination of Cis and MW radiation has significantly inhibited the growth of the A2780 and A2780CP cell lines in comparison with Cis-control groups. The percentages of early apoptosis induced by Cis+MW was significantly increased in comparison with Cis alone. P53 expression was significantly upregulated after treatment with Cis+MW.
ConclusionIt can be concluded that MW radiation has been able to decrease the resistance of ovarian cancer cells to Cis and it may improve the chemotherapy protocol for ovarian cancer treatment.
Keywords: Microwave Radiation, Drug resistance, Ovarian cancer, Cisplatin, Apoptosis -
Pages 304-313Background
Quinoline and its derivatives display various biological activities based on versatility in designing a new drug class for medicinal applications. Hence, synthesizing innovative and varied derivatives of quinoline has gained considerable attention among chemists and biologists. This study evaluated the anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinolineon Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7) human breast cancer cells.
MethodsThe anti-proliferative effect of tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinoline was studied via MTT[3 0-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assays. A quantitative and qualitative study of apoptosis was carried out via flow cytometry and terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL). Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and immunoblotting analysis were employed to identify the expression level of genes and proteins involved in the apoptosis signaling pathway.
ResultsThe synthesized compound reduced 50% of cell growth at concentrations of 10 and7.5 μM during 24 and 48h, respectively, and induced apoptosis up to 30% in MCF-7 cancer cells. Regarding the gene expression level, Bcl-2 displayed considerable alleviation, whereas Bax expression increased significantly. Despite the remarkable increase in caspase 9 expression, there was no noticeable difference in the caspase 8 expression in treated cells compared to the control group. Western blotting data showed that the protein expression level of Bcl-2, pro-caspase 8, and 9 reduced. The protein content of Bax, cleaved-caspase 8, and 9 increased significantly, of which the protein level of cleaved-caspase 9 exhibited a tremendous rise in the treated group.
ConclusionThe newly synthesized tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinoline can be a promising organic compound for cancer treatment if its anti-cancer effect investigates by other types of breast cancer cells. In vivo studies should be used to investigate the anti-cancer efficiency of this compound.
Keywords: Quinoline, MCF-7, Breast cancer, PCR, Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis -
Pages 314-323Background
UTI (urinary tract infection) is a leading case of renal scarring. Most of nephrons are found in kidney cortex, so it is important for early diagnosis of scarring. In this study, we investigated if scarring affects GFR (glomerular filtration rate) and serum level of creatinine through dual multipurpose 99mTc-GH (99mTc-Glucoheptonate) scintigraphy in patients with UTI.
MethodsDuring this study 21 patients with UTI were studied by 99mTc-GH scan. For performing scintigraphy, the patient was injected by 370-555 MBq of 99mTc-GH and studied through two steps including dynamic (immediately after injection) and static (2-3h after injection) phases. The results were evaluated by appropriate analytical methods. Moreover, five patients were studied by both 99mTc-DMSA/GH (99mTc-dimercaptosuccinic acid and 99mTc-Glucoheptonate) to show 99mTc-GH scan is beneficial for detection of additional problems.
ResultsThe results showed that there is an association between right/left kidney scarring and related GFR. Furthermore,, the odds of decreased right and left kidney GFR with scarring is 12.64 and 11.89 times more than normal kidney, respectively. Also, there is a significant association between renal scarring and serum level of creatinine. The study showed that the odds of increased serum level of creatinine in patients with scarring are 6.75 times more than patients without scarring. Moreover, the survey of five patients with both 99mTc-DMSA/GH scans showed 99mTc-GH could be helpful with diagnosis of some renal problems as well as scarring.
ConclusionThrough this study by 99mTc-GH, it was demonstrated that kidney glomerular filtration rate and serum level of creatinine are associated with renal scarring. Furthermore, it was shown that 99mTc-GH scintigraphy could detect dilatation and abstraction of collection system in addition to renal scarring through static/dynamic renal scintigraphy.
Keywords: Glomerular Filtration Rate, Urinary Tract Infection, Radionuclide Imaging, Creatinine, Radiation Protection -
Pages 324-330Background
In 2020 the composition and procedure to elaborate a new formulation containing Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide and Rifampicin to treat tuberculosis in pediatric patients was published. The temperature and relative humidity in Tuberculosis-endemic countries are high, > 30 ºC and > 70% respectively and thus these meteorological conditions required a new dosage form. The objective of this work is to register changes in tablet quality and stability over time when exposed to different storage conditions according to ICH.
MethodsTablets were subjected to accelerated, long term and low relative humidity conditions. The effect of light was also tested. Quality was measured by evaluating weight changes tensile strength, disintegration time, and drug content. Hydrazine formation was also evaluated as it is considered a mutagenic degradation product.
ResultsTablets stored at low relative humidity showed the best stability. There was no statistically significant difference between tablets exposed to or protected from light. Moreover, the formation of Hydrazine was not detected during stability studies.
ConclusionThis new dosage form for treating Tuberculosis is stable and able to maintain its quality when appropriate storage conditions are used.
Keywords: Dispersible tablet, Quality control, Pediatric, Stability evaluation, Tuberculosis -
Pages 331-339Background
Ciprofloxacin (CIP) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, used to treat various bacterial infections. Administration of conventional oral dosage forms of CIP is associated with multiple challenges such as short residence time of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract which could reduce bioavailability and effectiveness of the drug. This study aimed to design and develop novel floating microspheres for the sustained release of CIP in the stomach over 24 hours after oral administration, besides evaluating the effect of different variables on the characteristics of developed microspheres.
MethodsMicrospheres were developed by the solvent-evaporation method utilizing cellulose acetate and polyvinyl alcohol, then characterized for physicochemical properties including bulk density, buoyancy, and entrapment efficacy. The drug-excipient compatibility was evaluated by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and the Scanning electron microscopy was used to observe the morphology of microspheres. The effects of the drug to polymer ratio, polymer concentration, and the pace of stirring through the preparation process, on the size and release rate were also evaluated.
ResultsMorphology analysis indicated round-shape microspheres with a mean particle size between 66-344 µm. The polydispersity index of prepared formulations was determined to be in the range of 0.129 to 0.230. It was observed that at higher polymer concentrations the drug release rate from microspheres decreased while the mean particle size increased. Increasing the drug to polymer ratio and decreasing the stirring speed increased the mean particle size. All formulations showed more than 70% cumulative drug release in the prolonged period of 24 h while remaining buoyant in the meantime. The formulations followed Higuchi and Korsmeyer-Peppas kinetics and release the drug by diffusion mechanism.
ConclusionBased on the results obtained from in vitro release study besides floating properties, the prepared microspheres could be considered suitable for enhanced sustained-release of CIP following the oral administration.
Keywords: Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, Cellulose acetate, Floating microspheres, Gastro-retentive drug delivery systems, Solvent-evaporation


